Page 189 - Soil Degradation, Conservation and Remediation
P. 189
178 6 Soil Pollution
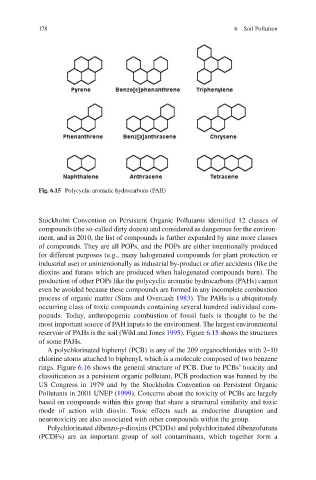
Fig. 6.15 Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH)
Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants identified 12 classes of
compounds (the so-called dirty dozen) and considered as dangerous for the environ-
ment, and in 2010, the list of compounds is further expanded by nine more classes
of compounds. They are all POPs, and the POPs are either intentionally produced
for different purposes (e.g., many halogenated compounds for plant protection or
industrial use) or unintentionally as industrial by-product or after accidents (like the
dioxins and furans which are produced when halogenated compounds burn). The
production of other POPs like the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) cannot
even be avoided because these compounds are formed in any incomplete combustion
process of organic matter (Sims and Overcash 1983 ). The PAHs is a ubiquitously
occurring class of toxic compounds containing several hundred individual com-
pounds. Today, anthropogenic combustion of fossil fuels is thought to be the
most important source of PAH inputs to the environment. The largest environmental
reservoir of PAHs is the soil ( Wild and Jones 1995 ). Figure 6.15 shows the structures
of some PAHs.
A polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) is any of the 209 organochlorides with 2–10
chlorine atoms attached to biphenyl, which is a molecule composed of two benzene
rings. Figure 6.16 shows the general structure of PCB. Due to PCBs’ toxicity and
classification as a persistent organic pollutant, PCB production was banned by the
US Congress in 1979 and by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic
Pollutants in 2001 UNEP ( 1999 ). Concerns about the toxicity of PCBs are largely
based on compounds within this group that share a structural similarity and toxic
mode of action with dioxin. Toxic effects such as endocrine disruption and
neurotoxicity are also associated with other compounds within the group.
Polychlorinated dibenzo- p -dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans
(PCDFs) are an important group of soil contaminants, which together form a