Page 190 - Soil Degradation, Conservation and Remediation
P. 190
6.2 Sources of Soil Pollutants 179
Fig. 6.16 Polychlorinated
biphenyl (PCB)
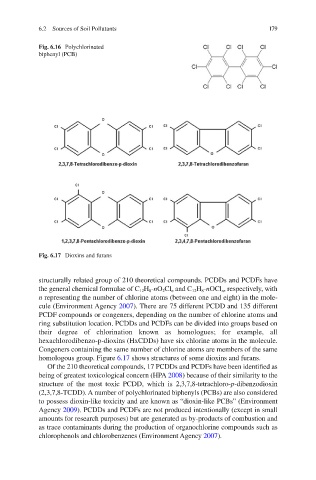
Fig. 6.17 Dioxins and furans
structurally related group of 210 theoretical compounds. PCDDs and PCDFs have
the general chemical formulae of C 12 H 8 - n O 2 Cl n and C 12 H 8 - n OCl n , respectively, with
n representing the number of chlorine atoms (between one and eight) in the mole-
cule (Environment Agency 2007 ). There are 75 different PCDD and 135 different
PCDF compounds or congeners, depending on the number of chlorine atoms and
ring substitution location. PCDDs and PCDFs can be divided into groups based on
their degree of chlorination known as homologues; for example, all
hexachlorodibenzo-p - dioxins (HxCDDs) have six chlorine atoms in the molecule.
Congeners containing the same number of chlorine atoms are members of the same
homologous group. Figure 6.17 shows structures of some dioxins and furans.
Of the 210 theoretical compounds, 17 PCDDs and PCDFs have been identifi ed as
being of greatest toxicological concern (HPA 2008 ) because of their similarity to the
structure of the most toxic PCDD, which is 2,3,7,8-tetrachloro- p -dibenzodioxin
(2,3,7,8-TCDD). A number of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are also considered
to possess dioxin-like toxicity and are known as “dioxin-like PCBs” (Environment
Agency 2009 ). PCDDs and PCDFs are not produced intentionally (except in small
amounts for research purposes) but are generated as by-products of combustion and
as trace contaminants during the production of organochlorine compounds such as
chlorophenols and chlorobenzenes (Environment Agency 2007 ).