Page 380 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 380
Patterns in surface water 367
400
TP>0.05 mg P l -1
No. of lakes = 26
300
200
100
0
400
TP>0.5 mg P l -1
No. of lakes = 53
TP (% of winter) 200
300
100
6642 6642 6642
0
J F M A M J J A S O N D
Month
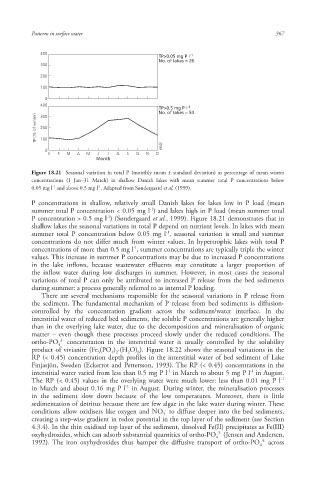
Figure 18.21 Seasonal variation in total P (monthly mean ± standard deviation ) as percentage of mean winter
concentrations (1 Jan–31 March) in shallow Danish lakes with mean summer total P concentrations below
-1
-1
0.05 mg l and above 0.5 mg l . Adapted from Søndergaard et al. (1999).
P concentrations in shallow, relatively small Danish lakes for lakes low in P load (mean
-1
summer total P concentration < 0.05 mg l ) and lakes high in P load (mean summer total
-1
P concentration > 0.5 mg l ) (Søndergaard et al., 1999). Figure 18.21 demonstrates that in
shallow lakes the seasonal variations in total P depend on nutrient levels. In lakes with mean
-1
summer total P concentration below 0.05 mg l , seasonal variation is small and summer
concentrations do not differ much from winter values. In hypertrophic lakes with total P
-1
concentrations of more than 0.5 mg l , summer concentrations are typically triple the winter
values. This increase in summer P concentrations may be due to increased P concentrations
in the lake inflows, because wastewater effluents may constitute a larger proportion of
the inflow water during low discharges in summer. However, in most cases the seasonal
variations of total P can only be attributed to increased P release from the bed sediments
during summer: a process generally referred to as internal P loading.
There are several mechanisms responsible for the seasonal variations in P release from
the sediment . The fundamental mechanism of P release from bed sediments is diffusion-
controlled by the concentration gradient across the sediment/water interface. In the
interstitial water of reduced bed sediments, the soluble P concentrations are generally higher
than in the overlying lake water, due to the decomposition and mineralisation of organic
matter – even though these processes proceed slowly under the reduced conditions. The
3-
ortho-PO concentration in the interstitial water is usually controlled by the solubility
4
product of vivianite (Fe (PO ) ·(H O) ). Figure 18.22 shows the seasonal variations in the
3 4 2 2 8
RP (< 0.45) concentration depth profiles in the interstitial water of bed sediment of Lake
Finjasjön, Sweden (Eckerrot and Pettersson, 1993). The RP (< 0.45) concentrations in the
-1
-1
interstitial water varied from less than 0.5 mg P l in March to about 5 mg P l in August.
-1
The RP (< 0.45) values in the overlying water were much lower: less than 0.01 mg P l
-1
in March and about 0.16 mg P l in August. During winter, the mineralisation processes
in the sediment slow down because of the low temperatures. Moreover, there is little
sedimentation of detritus because there are few algae in the lake water during winter. These
-
conditions allow oxidisers like oxygen and NO to diffuse deeper into the bed sediments,
3
creating a step-wise gradient in redox potential in the top layer of the sediment (see Section
4.3.4). In the thin oxidised top layer of the sediment, dissolved Fe(II) precipitates as Fe(III)
3-
oxyhydroxides , which can adsorb substantial quantities of ortho-PO (Jensen and Andersen,
4
3-
1992). The iron oxyhydroxides thus hamper the diffusive transport of ortho-PO across
4
10/1/2013 6:47:49 PM
Soil and Water.indd 379
Soil and Water.indd 379 10/1/2013 6:47:49 PM