Page 415 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 415
402 Soil and Water Contamination
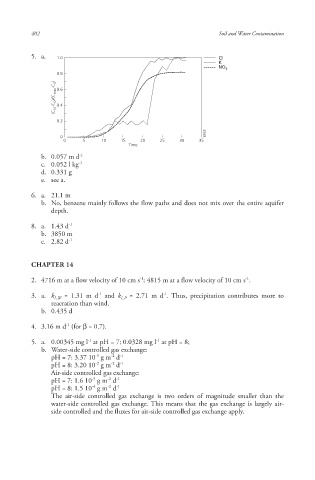
5. a. 1.0 Cl
K
NO 3
0.8
(C (t) -C 0 )/(C max -C 0 ) 0.6
0.4
0.2
6955
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
Time
b. 0.057 m d -1
c. 0.052 l kg -1
d. 0.331 g
e. see a.
6. a. 21.1 m
b. No, benzene mainly follows the flow paths and does not mix over the entire aquifer
depth.
8. a. 1.43 d -1
b. 3850 m
c. 2.82 d -1
CHAPTER 14
-1
-1
2. 4716 m at a flow velocity of 10 cm s ; 4815 m at a flow velocity of 10 cm s .
-1
-1
3. a. k = 1.31 m d and k = 2.71 m d . Thus, precipitation contributes more to
L,W L,P
reaeration than wind.
b. 0.435 d
-1
4. 3.16 m d (for β = 0.7).
-1
-1
5. a. 0.00345 mg l at pH = 7; 0.0328 mg l at pH = 8;
b. Water-side controlled gas exchange:
-3
-2
pH = 7: 3.37 10 g m d -1
-2
-2
pH = 8: 3.20 10 g m d -1
Air-side controlled gas exchange:
-5
-2
pH = 7: 1.6 10 g m d -1
-4
-2
pH = 8: 1.5 10 g m d -1
The air-side controlled gas exchange is two orders of magnitude smaller than the
water-side controlled gas exchange. This means that the gas exchange is largely air-
side controlled and the fluxes for air-side controlled gas exchange apply.
10/1/2013 6:47:54 PM
Soil and Water.indd 414 10/1/2013 6:47:54 PM
Soil and Water.indd 414