Page 414 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 414
Answers to exercises 401
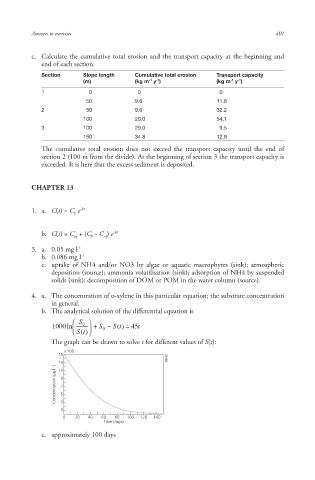
c. Calculate the cumulative total erosion and the transport capacity at the beginning and
end of each section.
Section Slope length Cumulative total erosion Transport capacity
-1
(m) (kg m y ) (kg m y )
-1
-1
-1
1 0 0 0
50 9.6 11.8
2 50 9.6 32.2
100 29.0 54.1
3 100 29.0 9.5
150 34.8 12.9
The cumulative total erosion does not exceed the transport capacity until the end of
section 2 (100 m from the divide). At the beginning of section 3 the transport capacity is
exceeded. It is here that the excess sediment is deposited.
CHAPTER 13
1. a. C(t) = C e -kt
0
b. C(t) = C + (C - C ) e -kt
eq 0 eq
3. a. 0.05 mg l -1
b. 0.086 mg l -1
c. uptake of NH4 and/or NO3 by algae or aquatic macrophytes (sink); atmospheric
deposition (source); ammonia volatilisation (sink); adsorption of NH4 by suspended
solids (sink); decomposition of DOM or POM in the water column (source).
4. a. The concentration of o-xylene in this particular equation; the substrate concentration
in general.
b. The analytical solution of the differential equation is
S 0
1000 ln S 0 S( t) 45 t
S( t)
The graph can be drawn to solve t for different values of S(t):
c. approximately 100 days
10/1/2013 6:47:54 PM
Soil and Water.indd 413 10/1/2013 6:47:54 PM
Soil and Water.indd 413