Page 112 - Solar Power in Building Design The Engineer's Complete Design Resource
P. 112
82 SOLAR POWER SYSTEM DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
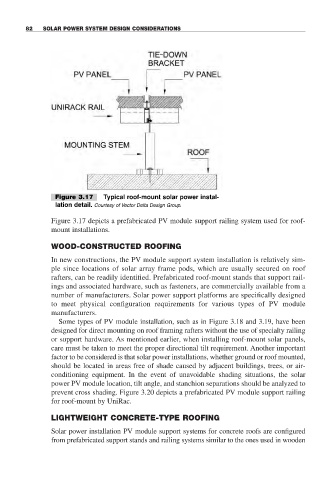
Figure 3.17 Typical roof-mount solar power instal-
lation detail. Courtesy of Vector Delta Design Group.
Figure 3.17 depicts a prefabricated PV module support railing system used for roof-
mount installations.
WOOD-CONSTRUCTED ROOFING
In new constructions, the PV module support system installation is relatively sim-
ple since locations of solar array frame pods, which are usually secured on roof
rafters, can be readily identified. Prefabricated roof-mount stands that support rail-
ings and associated hardware, such as fasteners, are commercially available from a
number of manufacturers. Solar power support platforms are specifically designed
to meet physical configuration requirements for various types of PV module
manufacturers.
Some types of PV module installation, such as in Figure 3.18 and 3.19, have been
designed for direct mounting on roof framing rafters without the use of specialty railing
or support hardware. As mentioned earlier, when installing roof-mount solar panels,
care must be taken to meet the proper directional tilt requirement. Another important
factor to be considered is that solar power installations, whether ground or roof mounted,
should be located in areas free of shade caused by adjacent buildings, trees, or air-
conditioning equipment. In the event of unavoidable shading situations, the solar
power PV module location, tilt angle, and stanchion separations should be analyzed to
prevent cross shading. Figure 3.20 depicts a prefabricated PV module support railing
for roof-mount by UniRac.
LIGHTWEIGHT CONCRETE-TYPE ROOFING
Solar power installation PV module support systems for concrete roofs are configured
from prefabricated support stands and railing systems similar to the ones used in wooden