Page 106 - Solid Waste Analysis and Minimization a Systems Approach
P. 106
84 DEPLOYMENT ALTERNATIVES
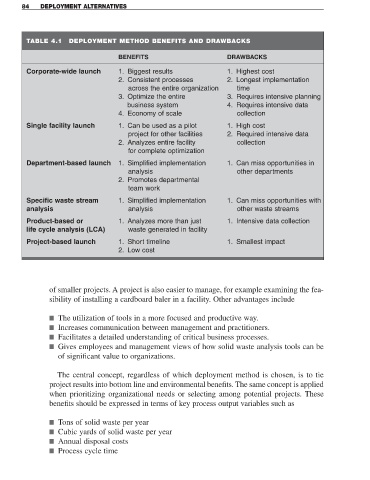
TABLE 4.1 DEPLOYMENT METHOD BENEFITS AND DRAWBACKS
BENEFITS DRAWBACKS
Corporate-wide launch 1. Biggest results 1. Highest cost
2. Consistent processes 2. Longest implementation
across the entire organization time
3. Optimize the entire 3. Requires intensive planning
business system 4. Requires intensive data
4. Economy of scale collection
Single facility launch 1. Can be used as a pilot 1. High cost
project for other facilities 2. Required intensive data
2. Analyzes entire facility collection
for complete optimization
Department-based launch 1. Simplified implementation 1. Can miss opportunities in
analysis other departments
2. Promotes departmental
team work
Specific waste stream 1. Simplified implementation 1. Can miss opportunities with
analysis analysis other waste streams
Product-based or 1. Analyzes more than just 1. Intensive data collection
life cycle analysis (LCA) waste generated in facility
Project-based launch 1. Short timeline 1. Smallest impact
2. Low cost
of smaller projects. A project is also easier to manage, for example examining the fea-
sibility of installing a cardboard baler in a facility. Other advantages include
■ The utilization of tools in a more focused and productive way.
■ Increases communication between management and practitioners.
■ Facilitates a detailed understanding of critical business processes.
■ Gives employees and management views of how solid waste analysis tools can be
of significant value to organizations.
The central concept, regardless of which deployment method is chosen, is to tie
project results into bottom line and environmental benefits. The same concept is applied
when prioritizing organizational needs or selecting among potential projects. These
benefits should be expressed in terms of key process output variables such as
■ Tons of solid waste per year
■ Cubic yards of solid waste per year
■ Annual disposal costs
■ Process cycle time