Page 210 - Standard Handbook Petroleum Natural Gas Engineering VOLUME2
P. 210
Formation Evaluation 179
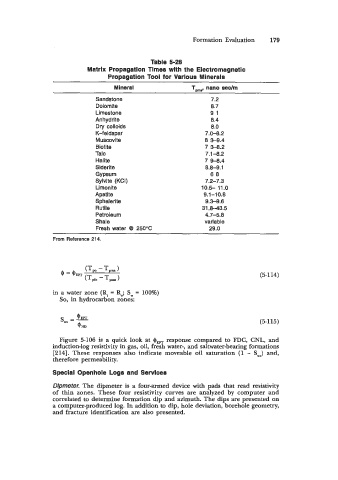
Table 5-28
Matrlx Propagatlon limes with the Electromagnetic
Propagation Tool for Varlous Minerals
~~
Mineral Tpma, nano sedm
Sandstone 7.2
Dolomite 8.7
Limestone 91
Anhydrite 8.4
Dry colloids 8.0
K-feldspar 7.0-8.2
Muscovite 8 3-9.4
Biotite 7 3-8.2
Talc 7.1-8.2
Halite 7 9-8.4
Siderite 8.8-9.1
Gypsum 68
Sylvite (KCI) 7.2-7.3
Limonite 10.5- 11.0
Apatite 9.1-1 0.8
Sphalerite 9.3-9.6
Rutile 31.843.5
Petroleum 4.7-5.8
Shale variable
Fresh water @I 250°C 29.0
From Reference 214.
(5-114)
in a water zone (R, = Ro; Sw = 100%)
So, in hydrocarbon zones:
s, = - (5-115)
$EFT
$m
Figure 5-106 is a quick look at response compared to FDC, CNL, and
induction-log resistivity in gas, oil, fresh water-, and saltwater-bearing formations
[214]. These responses also indicate moveable oil saturation (1 - S,) and,
therefore permeability.
Special Openhole Logs and Services
Dipmeter. The dipmeter is a four-armed device with pads that read resistivity
of thin zones. These four resistivity curves are analyzed by computer and
correlated to determine formation dip and azimuth. The dips are presented on
a computer-produced log. In addition to dip, hole deviation, borehole geometry,
and fracture identification are also presented.