Page 124 - Steam Turbines Design, Applications, and Rerating
P. 124
Rotors for Reaction Turbines 105
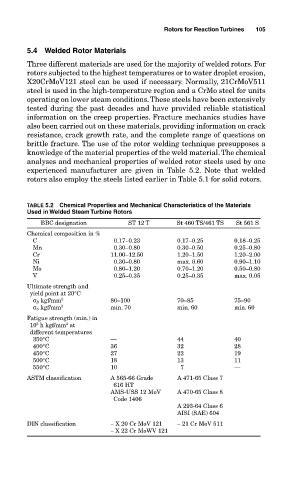
5.4 Welded Rotor Materials
Three different materials are used for the majority of welded rotors. For
rotors subjected to the highest temperatures or to water droplet erosion,
X20CrMoV121 steel can be used if necessary. Normally, 21CrMoV511
steel is used in the high-temperature region and a CrMo steel for units
operating on lower steam conditions.These steels have been extensively
tested during the past decades and have provided reliable statistical
information on the creep properties. Fracture mechanics studies have
also been carried out on these materials, providing information on crack
resistance, crack growth rate, and the complete range of questions on
brittle fracture. The use of the rotor welding technique presupposes a
knowledge of the material properties of the weld material.The chemical
analyses and mechanical properties of welded rotor steels used by one
experienced manufacturer are given in Table 5.2. Note that welded
rotors also employ the steels listed earlier in Table 5.1 for solid rotors.
TABLE 5.2 Chemical Properties and Mechanical Characteristics of the Materials
Used in Welded Steam Turbine Rotors
BBC designation ST 12 T St 460 TS/461 TS St 561 S
Chemical composition in %
C 0.17–0.23 0.17–0.25 0.18–0.25
Mn 0.30–0.80 0.30–0.50 0.25–0.80
Cr 11.00–12.50 1.20–1.50 1.20–2.00
Ni 0.30–0.80 max. 0.60 0.90–1.10
Mo 0.80–1.20 0.70–1.20 0.50–0.80
V 0.25–0.35 0.25–0.35 max. 0.05
Ultimate strength and
yield point at 20°C
σ B kgf/mm 2 80–100 70–85 75–90
σ S kgf/mm 2 min. 70 min. 60 min. 60
Fatigue strength (min.) in
2
5
10 h kgf/mm at
different temperatures
350°C — 44 40
400°C 36 32 28
450°C 27 22 19
500°C 18 13 11
550°C 10 7 —
ASTM classification A 565-66 Grade A 471-65 Class 7
616 HT
AMS-USS 12 MoV A 470-65 Class 8
Code 1406
A 293-64 Class 6
AISI (SAE) 604
DIN classification ∼ X 20 Cr MoV 121 ∼ 21 Cr MoV 511
∼ X 22 Cr MoWV 121