Page 329 - Steam Turbines Design, Applications, and Rerating
P. 329
Shortcut Graphical Methods of Turbine Selection 303
(b)
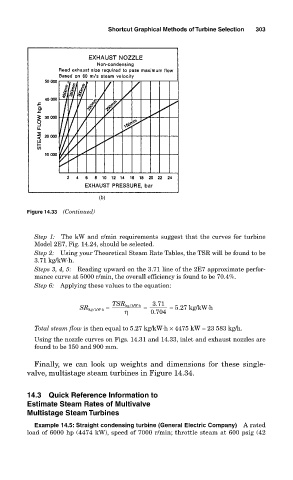
Figure 14.33 (Continued)
Step 1: The kW and r/min requirements suggest that the curves for turbine
Model 2E7, Fig. 14.24, should be selected.
Step 2: Using your Theoretical Steam Rate Tables, the TSR will be found to be
3.71 kg/kW⋅h.
Steps 3, 4, 5: Reading upward on the 3.71 line of the 2E7 approximate perfor-
mance curve at 5000 r/min, the overall efficiency is found to be 70.4%.
Step 6: Applying these values to the equation:
3.71
TSR kg/kW⋅h
SR kg/kW⋅h = = = 5.27 kg/kW⋅h
η 0.704
Total steam flow is then equal to 5.27 kg/kW⋅h × 4475 kW = 23 583 kg/h.
Using the nozzle curves on Figs. 14.31 and 14.33, inlet and exhaust nozzles are
found to be 150 and 900 mm.
Finally, we can look up weights and dimensions for these single-
valve, multistage steam turbines in Figure 14.34.
14.3 Quick Reference Information to
Estimate Steam Rates of Multivalve
Multistage Steam Turbines
Example 14.5: Straight condensing turbine (General Electric Company) A rated
load of 6000 hp (4474 kW), speed of 7000 r/min; throttle steam at 600 psig (42