Page 242 - Strategies and Applications in Quantum Chemistry From Molecular Astrophysics to Molecular Engineer
P. 242
CASE STUDIES OF ELECTROSTATIC PROPERTIES OF SMALL MOLECULES 225
rotational constants for the protonated species [28] which were used by Rice et al. [29] in
their theoretical study to support protonation on oxygen. This result has been recently
confirmed by Ekern et al. [30], who report, however, that this prediction is very sensitive
to the level of electron correlation introduced in the calculations : at MP3, MP4SDQ and
QCISD(T) levels, O-protonation is preferred, whereas in the MP2 and MP4SDTQ cases,
N-protonation is predicted. Actually, the fact that the protonated species is a difficult
case for quantum chemistry is not unexpected on the basis of the sensitivity of the
calculated dipole moment and MEP of this compound upon the level of electron correlation
introduced.
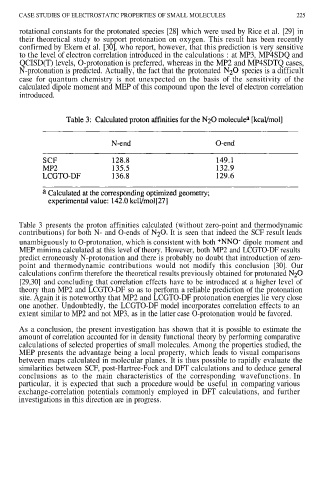
Table 3 presents the proton affinities calculated (without zero-point and thermodynamic
contributions) for both N- and O-ends of It is seen that indeed the SCF result leads
unambiguously to O-protonation, which is consistent with both dipole moment and
MEP minima calculated at this level of theory. However, both MP2 and LCGTO-DF results
predict erroneously N-protonation and there is probably no doubt that introduction of zero-
point and thermodynamic contributions would not modify this conclusion [30]. Our
calculations confirm therefore the theoretical results previously obtained for protonated
[29,30] and concluding that correlation effects have to be introduced at a higher level of
theory than MP2 and LCGTO-DF so as to perform a reliable prediction of the protonation
site. Again it is noteworthy that MP2 and LCGTO-DF protonation energies lie very close
one another. Undoubtedly, the LCGTO-DF model incorporates correlation effects to an
extent similar to MP2 and not MP3, as in the latter case O-protonation would be favored.
As a conclusion, the present investigation has shown that it is possible to estimate the
amount of correlation accounted for in density functional theory by performing comparative
calculations of selected properties of small molecules. Among the properties studied, the
MEP presents the advantage being a local property, which leads to visual comparisons
between maps calculated in molecular planes. It is thus possible to rapidly evaluate the
similarities between SCF, post-Hartree-Fock and DFT calculations and to deduce general
conclusions as to the main characteristics of the corresponding wavefunctions. In
particular, it is expected that such a procedure would be useful in comparing various
exchange-correlation potentials commonly employed in DFT calculations, and further
investigations in this direction are in progress.