Page 290 - Strategies and Applications in Quantum Chemistry From Molecular Astrophysics to Molecular Engineer
P. 290
AB INITIO CALCULATIONS OF POLARIZABILITIES IN MOLECULES 273
orbital which would be the relevant combination (a contracted STO). In fact, the
hydrogenic model does not apply exactly to any polyelectronic atom, so we let the
coefficients of the combination vary freely, as new variational parameters, in the
CPHF equations.
Moreover according to such a model, the same exponent is used in each perturbed
wavefunction, keeping the value of the non–perturbed wavefunction.
We propose to keep the same value of in both polarization functions and
but to dissociate their value from that of the zeroth order basis set which
is taken in the literature once for all so as to describe the system for the best; let be
this value. On the basis of the Hylleraas variation principle, we will determine the
suitable value for the hydrogenic scale factor in the polarization functions derived
from and after optimization with respect to maximum polarizability.
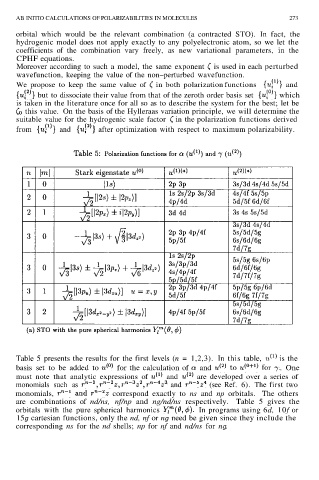
Table 5 presents the results for the first levels (n = 1,2,3). In this table, is the
basis set to be added to for the calculation of and . One
must note that analytic expressions of and are developed over a series of
monomials such as and (see Ref. 6). The first two
monomials, correspond exactly to ns and np orbitals. The others
are combinations of nd/ns, nf/np and ng/nd/ns respectively. Table 5 gives the
orbitals with the pure spherical harmonics In programs using 6d, 10f or
15g cartesian functions, only the nd, nf or ng need be given since they include the
corresponding ns for the nd shells; np for nf and nd/ns for ng.