Page 11 - Structural Steel Designers Handbook AISC, AASHTO, AISI, ASTM, and ASCE-07 Design Standards
P. 11
Brockenbrough_Ch01.qxd 9/29/05 4:59 PM Page 1.9
PROPERTIES OF STRUCTURAL STEELS AND EFFECTS OF STEELMAKING AND FABRICATION
STRUCTURAL STEELS, STEELMAKING, AND FABRICATION 1.9
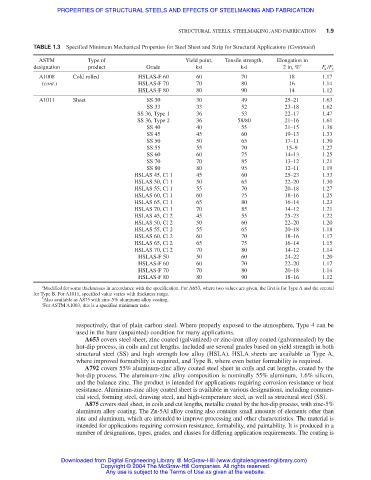
TABLE 1.3 Specified Minimum Mechanical Properties for Steel Sheet and Strip for Structural Applications (Continued)
ASTM Type of Yield point, Tensile strength, Elongation in
designation product Grade ksi ksi 2 in, % a F u /F y
A1008 Cold rolled HSLAS-F 60 60 70 18 1.17
(cont.) HSLAS-F 70 70 80 16 1.14
HSLAS-F 80 80 90 14 1.12
A1011 Sheet SS 30 30 49 25–21 1.63
SS 33 33 52 23–18 1.62
SS 36, Type 1 36 53 22–17 1.47
SS 36, Type 2 36 58/80 21–16 1.61
SS 40 40 55 21–15 1.38
SS 45 45 60 19–13 1.33
SS 50 50 65 17–11 1.30
SS 55 55 70 15–9 1.27
SS 60 60 75 14–13 1.25
SS 70 70 85 13–12 1.21
SS 80 80 95 12–11 1.19
HSLAS 45, Cl 1 45 60 25–23 1.33
HSLAS 50, Cl 1 50 65 22–20 1.30
HSLAS 55, Cl 1 55 70 20–18 1.27
HSLAS 60, Cl 1 60 75 18–16 1.25
HSLAS 65, Cl 1 65 80 16–14 1.23
HSLAS 70, Cl 1 70 85 14–12 1.21
HSLAS 45, Cl 2 45 55 25–23 1.22
HSLAS 50, Cl 2 50 60 22–20 1.20
HSLAS 55, Cl 2 55 65 20–18 1.18
HSLAS 60, Cl 2 60 70 18–16 1.17
HSLAS 65, Cl 2 65 75 16–14 1.15
HSLAS 70, Cl 2 70 80 14–12 1.14
HSLAS-F 50 50 60 24–22 1.20
HSLAS-F 60 60 70 22–20 1.17
HSLAS-F 70 70 80 20–18 1.14
HSLAS-F 80 80 90 18–16 1.12
a
Modified for some thicknesses in accordance with the specification. For A653, where two values are given, the first is for Type A and the second
for Type B. For A1011, specified value varies with thickness range.
b
Also available as A875 with zinc-5% aluminum alloy coating.
c
For ASTM A1003, this is a specified minimum ratio.
respectively, that of plain carbon steel. Where properly exposed to the atmosphere, Type 4 can be
used in the bare (unpainted) condition for many applications.
A653 covers steel sheet, zinc coated (galvanized) or zinc-iron alloy coated (galvannealed) by the
hot-dip process, in coils and cut lengths. Included are several grades based on yield strength in both
structural steel (SS) and high strength low alloy (HSLA). HSLA sheets are available as Type A,
where improved formability is required, and Type B, where even better formability is required.
A792 covers 55% aluminum-zinc alloy coated steel sheet in coils and cut lengths, coated by the
hot-dip process. The aluminum-zinc alloy composition is nominally 55% aluminum, 1.6% silicon,
and the balance zinc. The product is intended for applications requiring corrosion resistance or heat
resistance. Aluminum-zinc alloy coated sheet is available in various designations, including commer-
cial steel, forming steel, drawing steel, and high-temperature steel, as well as structural steel (SS).
A875 covers steel sheet, in coils and cut lengths, metallic coated by the hot-dip process, with zinc-5%
aluminum alloy coating. The Zn-5Al alloy coating also contains small amounts of elements other than
zinc and aluminum, which are intended to improve processing and other characteristics. The material is
intended for applications requiring corrosion resistance, formability, and paintability. It is produced in a
number of designations, types, grades, and classes for differing application requirements. The coating is
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.