Page 12 - Structural Steel Designers Handbook AISC, AASHTO, AISI, ASTM, and ASCE-07 Design Standards
P. 12
Brockenbrough_Ch01.qxd 9/29/05 4:59 PM Page 1.10
PROPERTIES OF STRUCTURAL STEELS AND EFFECTS OF STEELMAKING AND FABRICATION
1.10 CHAPTER ONE
produced as two types—zinc-5% aluminum-mischmetal alloy (Type I) and zinc-5% aluminum-0.1%
magnesium alloy (Type II)—in two coating structures (classes), and in several coating weight designa-
tions. Mechanical properties are generally similar to those of A653.
A1003 covers coated steel sheet used in the manufacture of cold-formed framing members, such
as, but not limited to, studs, joists, purlins, girts, and track. The sheet steel used for cold-formed
framing members includes metallic coated, painted metallic coated, and painted nonmetallic coated.
The grade designations use the following suffix indicators: H, high ductility; L, low ductility; and
NS, nonstructural. H and L are associated with structural or load-bearing applications, and NS with
nonstructural or non-load-bearing applications.
A1008 covers cold-rolled structural steel (SS), high-strength low-alloy steel (HSLAS), and high-
strength low-alloy steel with improved formability (HSLAS-F), in coils and cut lengths. The steel is
fully deoxidized, made to fine-grain practice, and includes microalloying elements such as columbi-
um, vanadium, and zirconium. The steel may be treated to achieve inclusion control. Cold-rolled
steel sheet is supplied for either exposed or unexposed applications.
A1011 covers hot-rolled sheet and strip, in coils and cut lengths. The product is produced in a
number of designations, including SS, HSLAS, and HSLAS-F. The steel is fully deoxidized, made
to fine-grain practice, and includes microalloying elements such as columbium, vanadium, and zir-
conium. The steel may be treated to achieve inclusion control.
1.4 TUBING FOR STRUCTURAL APPLICATIONS
Structural tubing is being used more frequently in modern construction. Commonly referred to as hol-
low structural sections (HSS), it is often preferred to other steel members when resistance to torsion
is required and when a smooth, closed section is aesthetically desirable. In addition, structural tubing
may be the economical choice for compression members subjected to moderate to light loads. Square
and rectangular tubing is manufactured either by cold or hot forming welded or seamless round tub-
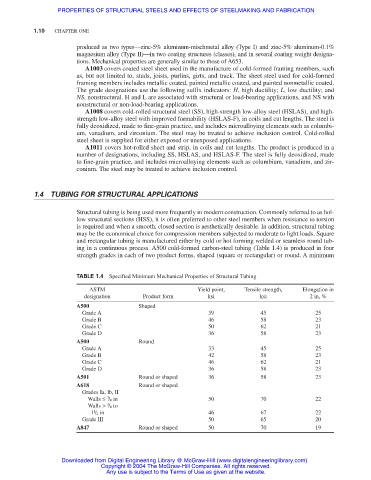
ing in a continuous process. A500 cold-formed carbon-steel tubing (Table 1.4) is produced in four
strength grades in each of two product forms, shaped (square or rectangular) or round. A minimum
TABLE 1.4 Specified Minimum Mechanical Properties of Structural Tubing
ASTM Yield point, Tensile strength, Elongation in
designation Product form ksi ksi 2 in, %
A500 Shaped
Grade A 39 45 25
Grade B 46 58 23
Grade C 50 62 21
Grade D 36 58 23
A500 Round
Grade A 33 45 25
Grade B 42 58 23
Grade C 46 62 21
Grade D 36 58 23
A501 Round or shaped 36 58 23
A618 Round or shaped
Grades Ia, lb, II
3
Walls ≤ / 4 in 50 70 22
3
Walls > / 4 to
1
1 / 2 in 46 67 22
Grade III 50 65 20
A847 Round or shaped 50 70 19
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.