Page 8 - Structural Steel Designers Handbook AISC, AASHTO, AISI, ASTM, and ASCE-07 Design Standards
P. 8
Brockenbrough_Ch01.qxd 9/29/05 4:59 PM Page 1.6
PROPERTIES OF STRUCTURAL STEELS AND EFFECTS OF STEELMAKING AND FABRICATION
1.6 CHAPTER ONE
Steels furnished to this specification can provide a resistance to atmospheric corrosion up to four
times that of structural carbon steel depending on the grade.
Constructional alloy steels are also frequently selected because of their ability to resist abra-
sion. For many types of abrasion, this resistance is related to hardness or tensile strength.
Therefore, constructional alloy steels may have nearly twice the resistance to abrasion provided
by carbon steel. Also available are numerous grades that have been heat treated to increase the
hardness even more.
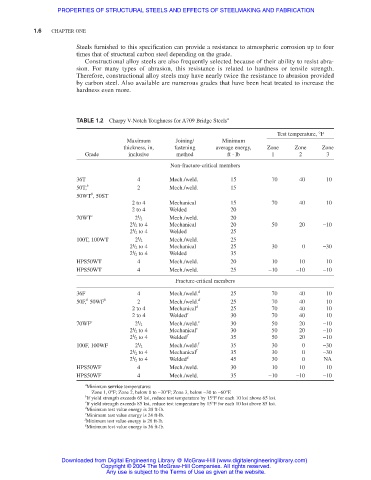
TABLE 1.2 Charpy V-Notch Toughness for A709 Bridge Steels a
Test temperature, °F
Maximum Joining/ Minimum
thickness, in, fastening average energy, Zone Zone Zone
Grade inclusive method ft ⋅ lb 1 2 3
Non-fracture-critical members
36T 4 Mech./weld. 15 70 40 10
50T, b 2 Mech./weld. 15
b
50WT , 50ST
2 to 4 Mechanical 15 70 40 10
2 to 4 Welded 20
1
70WT c 2 / 2 Mech./weld. 20
1
2 / 2 to 4 Mechanical 20 50 20 −10
2 / 2 to 4 Welded 25
1
1
100T, 100WT 2 / 2 Mech./weld. 25
2 / 2 to 4 Mechanical 25 30 0 −30
1
1
2 / 2 to 4 Welded 35
HPS50WT 4 Mech./weld. 20 10 10 10
HPS50WT 4 Mech./weld. 25 −10 −10 −10
Fracture-critical members
36F 4 Mech./weld. d 25 70 40 10
b
50F, 50WF b 2 Mech./weld. d 25 70 40 10
2 to 4 Mechanical d 25 70 40 10
2 to 4 Welded e 30 70 40 10
1
70WF c 2 / 2 Mech./weld. e 30 50 20 −10
1
2 / 2 to 4 Mechanical e 30 50 20 −10
1
2 / 2 to 4 Welded f 35 50 20 −10
1
100F, 100WF 2 / 2 Mech./weld. f 35 30 0 −30
1
2 / 2 to 4 Mechanical f 35 30 0 −30
2 / 2 to 4 Welded g 45 30 0 NA
1
HPS50WF 4 Mech./weld. 30 10 10 10
HPS50WF 4 Mech./weld. 35 −10 −10 −10
a
Minimum service temperatures:
Zone 1, 0°F; Zone 2, below 0 to −30°F; Zone 3, below −30 to −60°F.
b
If yield strength exceeds 65 ksi, reduce test temperature by 15°F for each 10 ksi above 65 ksi.
c
If yield strength exceeds 85 ksi, reduce test temperature by 15°F for each 10 ksi above 85 ksi.
d
Minimum test value energy is 20 ft-lb.
e
Minimum test value energy is 24 ft-lb.
f
Minimum test value energy is 28 ft-lb.
g
Minimum test value energy is 36 ft-lb.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.