Page 388 - Sustainable Cities and Communities Design Handbook
P. 388
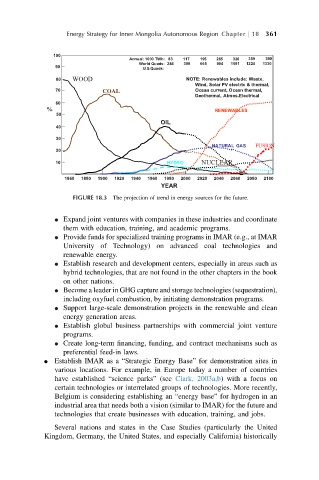
Energy Strategy for Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Chapter j 18 361
100
390
Annual: 1000 TWh: 83 117 195 265 320 359 390
World Quads: 284 399 665 904 1091 1224 1330
90 U.S.Quads:
80 WOOD NOTE: Renewables include: Waste,
Wind, Solar PV electric & thermal,
70 Ocean current, Ocean thermal,
COAL
Geothermal, Atmos.Electrical
60
RENEWABLES
%
50
OIL
40
30
NATURAL GAS FUSION
20
10 HYDRO NUCLEAR
1860 1880 1900 1920 1940 1960 1980 2000 2020 2040 2060 2080 2100
YEAR
FIGURE 18.3 The projection of trend in energy sources for the future.
l Expand joint ventures with companies in these industries and coordinate
them with education, training, and academic programs.
l Provide funds for specialized training programs in IMAR (e.g., at IMAR
University of Technology) on advanced coal technologies and
renewable energy.
l Establish research and development centers, especially in areas such as
hybrid technologies, that are not found in the other chapters in the book
on other nations.
l Become a leader in GHG capture and storage technologies (sequestration),
including oxyfuel combustion, by initiating demonstration programs.
l Support large-scale demonstration projects in the renewable and clean
energy generation areas.
l Establish global business partnerships with commercial joint venture
programs.
l Create long-term financing, funding, and contract mechanisms such as
preferential feed-in laws.
l Establish IMAR as a “Strategic Energy Base” for demonstration sites in
various locations. For example, in Europe today a number of countries
have established “science parks” (see Clark, 2003a,b) with a focus on
certain technologies or interrelated groups of technologies. More recently,
Belgium is considering establishing an “energy base” for hydrogen in an
industrial area that needs both a vision (similar to IMAR) for the future and
technologies that create businesses with education, training, and jobs.
Several nations and states in the Case Studies (particularly the United
Kingdom, Germany, the United States, and especially California) historically