Page 118 - Sustainable On-Site CHP Systems Design, Construction, and Operations
P. 118
96 CHP B a s i c s
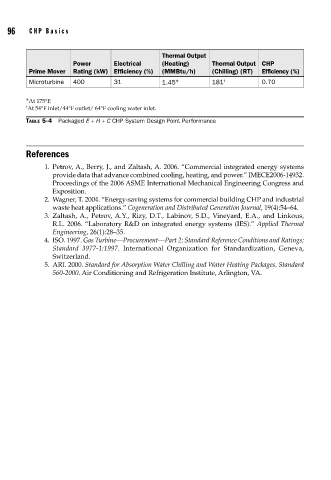
Thermal Output
Power Electrical (Heating) Thermal Output CHP
Prime Mover Rating (kW) Efficiency (%) (MMBtu/h) (Chilling) (RT) Efficiency (%)
Microturbine 400 31 1.45 ∗ 181 † 0.70
∗ At 175°F.
† At 54°F inlet/44°F outlet/ 64°F cooling water inlet.
TABLE 5-4 Packaged E + H + C CHP System Design Point Performance
References
1. Petrov, A., Berry, J., and Zaltash, A. 2006. “Commercial integrated energy systems
provide data that advance combined cooling, heating, and power.” IMECE2006-14932.
Proceedings of the 2006 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and
Exposition.
2. Wagner, T. 2004. “Energy-saving systems for commercial building CHP and industrial
waste heat applications.” Cogeneration and Distributed Generation Journal, 19(4):54–64.
3. Zaltash, A., Petrov, A.Y., Rizy, D.T., Labinov, S.D., Vineyard, E.A., and Linkous,
R.L. 2006. “Laboratory R&D on integrated energy systems (IES).” Applied Thermal
Engineering, 26(1):28–35.
4. ISO. 1997. Gas Turbine—Procurement—Part 2; Standard Reference Conditions and Ratings;
Standard 3977-1:1997. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva,
Switzerland.
5. ARI. 2000. Standard for Absorption Water Chilling and Water Heating Packages, Standard
560-2000. Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Institute, Arlington, VA.