Page 30 - Sustainable On-Site CHP Systems Design, Construction, and Operations
P. 30
Overview 9
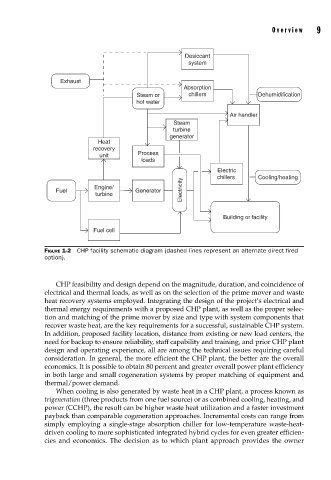
Desiccant
system
Exhaust
Absorption
Steam or chillers Dehumidification
hot water
Air handler
Steam
turbine
generator
Heat
recovery
unit Process
loads
Electric
chillers Cooling/heating
Engine/
Fuel Generator Electricity
turbine
Building or facility
Fuel cell
FIGURE 1-2 CHP facility schematic diagram (dashed lines represent an alternate direct fi red
option).
CHP feasibility and design depend on the magnitude, duration, and coincidence of
electrical and thermal loads, as well as on the selection of the prime mover and waste
heat recovery systems employed. Integrating the design of the project’s electrical and
thermal energy requirements with a proposed CHP plant, as well as the proper selec-
tion and matching of the prime mover by size and type with system components that
recover waste heat, are the key requirements for a successful, sustainable CHP system.
In addition, proposed facility location, distance from existing or new load centers, the
need for backup to ensure reliability, staff capability and training, and prior CHP plant
design and operating experience, all are among the technical issues requiring careful
consideration. In general, the more efficient the CHP plant, the better are the overall
economics. It is possible to obtain 80 percent and greater overall power plant efficiency
in both large and small cogeneration systems by proper matching of equipment and
thermal/power demand.
When cooling is also generated by waste heat in a CHP plant, a process known as
trigeneration (three products from one fuel source) or as combined cooling, heating, and
power (CCHP), the result can be higher waste heat utilization and a faster investment
payback than comparable cogeneration approaches. Incremental costs can range from
simply employing a single-stage absorption chiller for low-temperature waste-heat-
driven cooling to more sophisticated integrated hybrid cycles for even greater efficien-
cies and economics. The decision as to which plant approach provides the owner