Page 157 - Synthetic Fuels Handbook
P. 157
FUELS FROM COAL 143
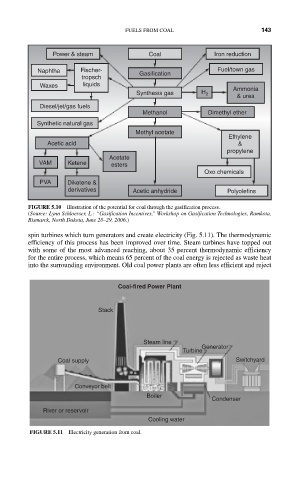
Power & steam Coal Iron reduction
Naphtha Fischer- Gasification Fuel/town gas
tropsch
Waxes liquids Ammonia
Synthesis gas H 2 & urea
Diesel/jet/gas fuels
Methanol Dimethyl ether
Synthetic natural gas
Methyl acetate
Ethylene
Acetic acid &
propylene
Acetate
VAM Ketene esters
Oxo chemicals
PVA Diketene &
derivatives Acetic anhydride Polyolefins
FIGURE 5.10 Illustration of the potential for coal through the gasification process.
(Source: Lynn Schloesser, L.: “Gasification Incentives,” Workshop on Gasification Technologies, Ramkota,
Bismarck, North Dakota, June 28–29, 2006.)
spin turbines which turn generators and create electricity (Fig. 5.11). The thermodynamic
efficiency of this process has been improved over time. Steam turbines have topped out
with some of the most advanced reaching, about 35 percent thermodynamic efficiency
for the entire process, which means 65 percent of the coal energy is rejected as waste heat
into the surrounding environment. Old coal power plants are often less efficient and reject
Coal-fired Power Plant
Stack
Steam line
Generator
Turbine
Coal supply Switchyard
Conveyor belt
Boiler
Condenser
River or reservoir
Cooling water
FIGURE 5.11 Electricity generation from coal.