Page 160 - Synthetic Fuels Handbook
P. 160
146 CHAPTER FIVE
plants, especially air emissions, and the potential for lower-cost control of green-
house gases than other coal-based systems. Fluctuations in the costs associated with
natural-gas-based power, which is viewed as a major competitor to coal based power,
can also play a role.
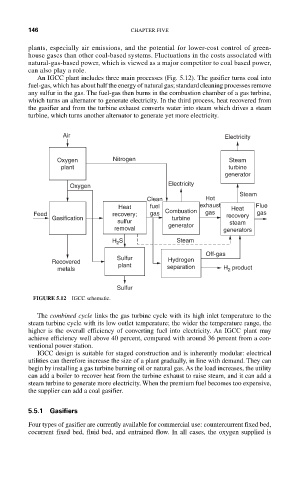
An IGCC plant includes three main processes (Fig. 5.12). The gasifier turns coal into
fuel-gas, which has about half the energy of natural gas; standard cleaning processes remove
any sulfur in the gas. The fuel-gas then burns in the combustion chamber of a gas turbine,
which turns an alternator to generate electricity. In the third process, heat recovered from
the gasifier and from the turbine exhaust converts water into steam which drives a steam
turbine, which turns another alternator to generate yet more electricity.
Air Electricity
Oxygen Nitrogen Steam
plant turbine
generator
Oxygen Electricity
Steam
Clean Hot
Heat fuel exhaust Heat Flue
Feed recovery; gas Combustion gas recovery gas
Gasification turbine
sulfur steam
removal generator generators
H S Steam
2
Off-gas
Sulfur Hydrogen
Recovered plant
metals separation H product
2
Sulfur
FIGURE 5.12 IGCC schematic.
The combined cycle links the gas turbine cycle with its high inlet temperature to the
steam turbine cycle with its low outlet temperature; the wider the temperature range, the
higher is the overall efficiency of converting fuel into electricity. An IGCC plant may
achieve efficiency well above 40 percent, compared with around 36 percent from a con-
ventional power station.
IGCC design is suitable for staged construction and is inherently modular: electrical
utilities can therefore increase the size of a plant gradually, in line with demand. They can
begin by installing a gas turbine burning oil or natural gas. As the load increases, the utility
can add a boiler to recover heat from the turbine exhaust to raise steam, and it can add a
steam turbine to generate more electricity. When the premium fuel becomes too expensive,
the supplier can add a coal gasifier.
5.5.1 Gasifiers
Four types of gasifier are currently available for commercial use: countercurrent fixed bed,
cocurrent fixed bed, fluid bed, and entrained flow. In all cases, the oxygen supplied is