Page 163 - Synthetic Fuels Handbook
P. 163
FUELS FROM COAL 149
Power & steam Coal Iron reduction
Naphtha Fischer- Gasification Fuel/town gas
tropsch
Waxes liquids Ammonia
Synthesis gas H 2 & urea
Diesel/jet/gas fuels
Methanol Dimethyl ether
Synthetic natural gas
Methyl acetate
Ethylene
Acetic acid &
propylene
Acetate
VAM Ketene esters
Oxo chemicals
PVA Diketene &
derivatives Acetic anhydride Polyolefins
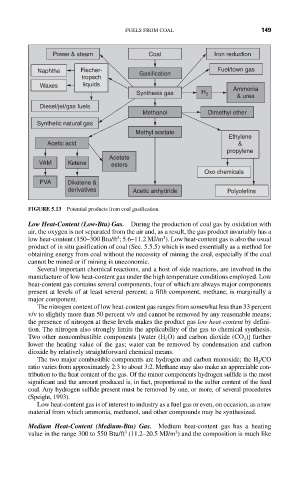
FIGURE 5.13 Potential products from coal gasification.
Low Heat-Content (Low-Btu) Gas. During the production of coal gas by oxidation with
air, the oxygen is not separated from the air and, as a result, the gas product invariably has a
3
3
low heat-content (150–300 Btu/ft ; 5.6–11.2 MJ/m ). Low heat-content gas is also the usual
product of in situ gasification of coal (Sec. 5.5.5) which is used essentially as a method for
obtaining energy from coal without the necessity of mining the coal, especially if the coal
cannot be mined or if mining is uneconomic.
Several important chemical reactions, and a host of side reactions, are involved in the
manufacture of low heat-content gas under the high temperature conditions employed. Low
heat-content gas contains several components, four of which are always major components
present at levels of at least several percent; a fifth component, methane, is marginally a
major component.
The nitrogen content of low heat-content gas ranges from somewhat less than 33 percent
v/v to slightly more than 50 percent v/v and cannot be removed by any reasonable means;
the presence of nitrogen at these levels makes the product gas low heat-content by defini-
tion. The nitrogen also strongly limits the applicability of the gas to chemical synthesis.
Two other noncombustible components [water (H O) and carbon dioxide (CO )] further
2
2
lower the heating value of the gas; water can be removed by condensation and carbon
dioxide by relatively straightforward chemical means.
The two major combustible components are hydrogen and carbon monoxide; the H /CO
2
ratio varies from approximately 2:3 to about 3:2. Methane may also make an appreciable con-
tribution to the heat content of the gas. Of the minor components hydrogen sulfide is the most
significant and the amount produced is, in fact, proportional to the sulfur content of the feed
coal. Any hydrogen sulfide present must be removed by one, or more, of several procedures
(Speight, 1993).
Low heat-content gas is of interest to industry as a fuel gas or even, on occasion, as a raw
material from which ammonia, methanol, and other compounds may be synthesized.
Medium Heat-Content (Medium-Btu) Gas. Medium heat-content gas has a heating
3
3
value in the range 300 to 550 Btu/ft (11.2–20.5 MJ/m ) and the composition is much like