Page 302 -
P. 302
chaPter 10 • object-oriented systems analysis and design Using Uml 269
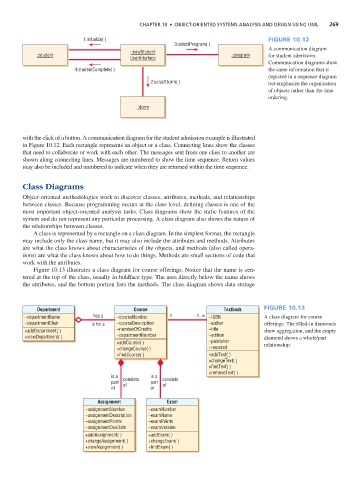
1:initialize( ) Figure 10.12
3:selectProgram( )
::newStudent A communication diagram
::student ::program for student admission.
UserInterface
Communication diagrams show
4:studentComplete( ) the same information that is
depicted in a sequence diagram
2:selectDorm( ) but emphasize the organization
of objects rather than the time
ordering.
::dorm
with the click of a button. A communication diagram for the student admission example is illustrated
in Figure 10.12. Each rectangle represents an object or a class. Connecting lines show the classes
that need to collaborate or work with each other. The messages sent from one class to another are
shown along connecting lines. Messages are numbered to show the time sequence. Return values
may also be included and numbered to indicate when they are returned within the time sequence.
Class Diagrams
Object-oriented methodologies work to discover classes, attributes, methods, and relationships
between classes. Because programming occurs at the class level, defining classes is one of the
most important object-oriented analysis tasks. Class diagrams show the static features of the
system and do not represent any particular processing. A class diagram also shows the nature of
the relationships between classes.
A class is represented by a rectangle on a class diagram. In the simplest format, the rectangle
may include only the class name, but it may also include the attributes and methods. Attributes
are what the class knows about characteristics of the objects, and methods (also called opera-
tions) are what the class knows about how to do things. Methods are small sections of code that
work with the attributes.
Figure 10.13 illustrates a class diagram for course offerings. Notice that the name is cen-
tered at the top of the class, usually in boldface type. The area directly below the name shows
the attributes, and the bottom portion lists the methods. The class diagram shows data storage
Department Course Textbook Figure 10.13
–departmentName has a –courseNumber 1 1.. –ISBN A class diagram for course
–departmentChair is for a –courseDescription –author offerings. The filled-in diamonds
+addDepartment( ) –numberOfCredits –title show aggregation, and the empty
+viewDepartment( ) –departmentNumber –edition diamond shows a whole/part
+addCourse( ) –publisher relationship.
+changeCourse( ) –required
+findCourse( ) +addText( )
+changeText( )
+findText( )
+removeText( )
is a consists is a consists
part of part of
of of
Assignment Exam
–assignmentNumber –examNumber
–assignmentDescription –examName
–assignmentPoints –examPoints
–assignmentDueDate –examVersion
+addAssignment( ) +addExam( )
+changeAssignment( ) +changeExam( )
+viewAssignment( ) +findExam( )