Page 201 - Tandem Techniques
P. 201
Page 184
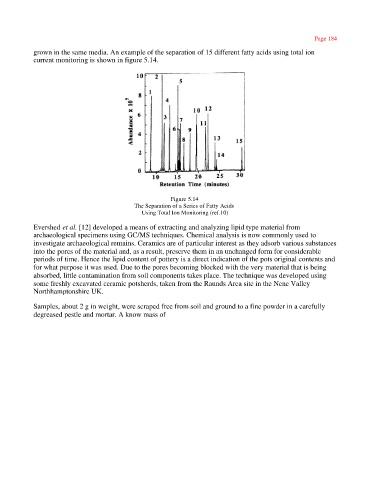
grown in the same media. An example of the separation of 15 different fatty acids using total ion
current monitoring is shown in figure 5.14.
Figure 5.14
The Separation of a Series of Fatty Acids
Using Total Ion Monitoring (ref.10)
Evershed et al. [12] developed a means of extracting and analyzing lipid type material from
archaeological specimens using GC/MS techniques. Chemical analysis is now commonly used to
investigate archaeological remains. Ceramics are of particular interest as they adsorb various substances
into the pores of the material and, as a result, preserve them in an unchanged form for considerable
periods of time. Hence the lipid content of pottery is a direct indication of the pots original contents and
for what purpose it was used. Due to the pores becoming blocked with the very material that is being
absorbed, little contamination from soil components takes place. The technique was developed using
some freshly excavated ceramic potsherds, taken from the Raunds Area site in the Nene Valley
Northhamptonshire UK.
Samples, about 2 g in weight, were scraped free from soil and ground to a fine powder in a carefully
degreased pestle and mortar. A know mass of