Page 236 - Tandem Techniques
P. 236
Page 219
A Combustion Interface for Isotope Ratio Monitoring with GC/MS
The use of a combustion process to determine the isotopic composition of gas chromatography eluents
was reported in the 1970s [50,51]. However, more recently, Meritt et al. [52] have carried out an
exhaustive examination of the method and from the results have suggested optimum conditions for a
GC/MS tandem system. The basic system comprised a gas chromatograph, a high-temperature oxidizer,
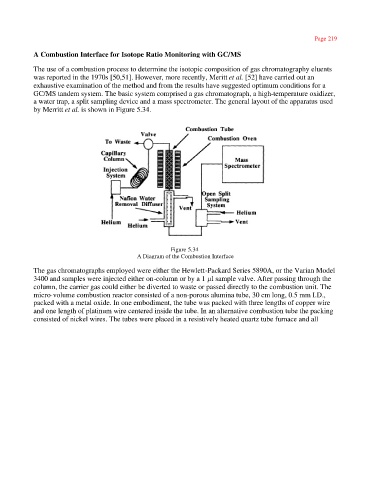
a water trap, a split sampling device and a mass spectrometer. The general layout of the apparatus used
by Merritt et al. is shown in Figure 5.34.
Figure 5.34
A Diagram of the Combustion Interface
The gas chromatographs employed were either the Hewlett-Packard Series 5890A, or the Varian Model
3400 and samples were injected either on-column or by a 1 µl sample valve. After passing through the
column, the carrier gas could either be diverted to waste or passed directly to the combustion unit. The
micro-volume combustion reactor consisted of a non-porous alumina tube, 30 cm long, 0.5 mm I.D.,
packed with a metal oxide. In one embodiment, the tube was packed with three lengths of copper wire
and one length of platinum wire centered inside the tube. In an alternative combustion tube the packing
consisted of nickel wires. The tubes were placed in a resistively heated quartz tube furnace and all