Page 238 - Tandem Techniques
P. 238
Page 221
instituted the collection of dust particles during orbit for analysis on return to earth. Microscopic
examination and elemental analysis has proved to be of limited value, and so means of identifying
particulate sources, by tests that would provide 'fingerprint' identification of source materials, were
consequently investigated.
Pyrolysis/GC/MS has been successfully applied to the study of a variety of biological materials [53],
including polysaccharides [54], lignins [55], and soils [56]. With these publications in mind, a
pyrolysis/GC/MS system was developed by Matney and Limero [57], that could provide
chromatographic and spectrographic patterns that might allow particulate source identification. The
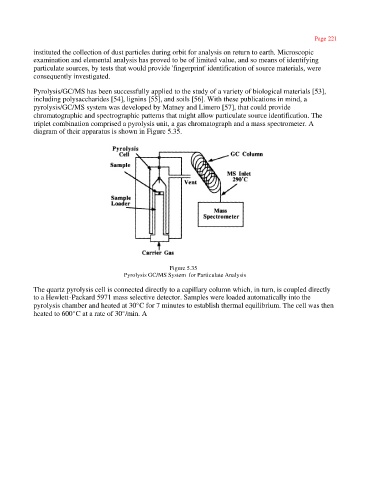
triplet combination comprised a pyrolysis unit, a gas chromatograph and a mass spectrometer. A
diagram of their apparatus is shown in Figure 5.35.
Figure 5.35
Pyrolysis GC/MS System for Particulate Analysis
The quartz pyrolysis cell is connected directly to a capillary column which, in turn, is coupled directly
to a Hewlett-Packard 5971 mass selective detector. Samples were loaded automatically into the
pyrolysis chamber and heated at 30°C for 7 minutes to establish thermal equilibrium. The cell was then
heated to 600°C at a rate of 30°/min. A