Page 104 - The Biochemistry of Inorganic Polyphosphates
P. 104
WU095/Kulaev
WU095-06
Enzymes of polyphosphate biosynthesis and degradation
88 March 9, 2004 15:32 Char Count= 0
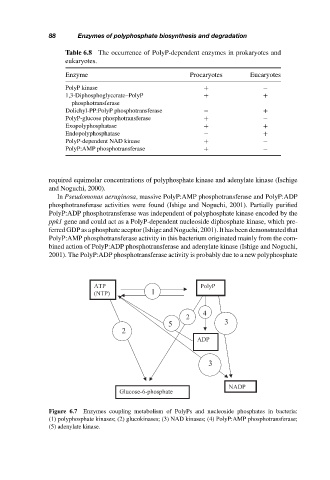
Table 6.8 The occurrence of PolyP-dependent enzymes in prokaryotes and
eukaryotes.
Enzyme Procaryotes Eucaryotes
PolyP kinase + −
1,3-Diphosphoglycerate–PolyP + +
phosphotransferase
Dolichyl-PP:PolyP phosphotransferase − +
PolyP-glucose phosphotransferase + −
Exopolyphosphatase + +
Endopolyphosphatase − +
PolyP-dependent NAD kinase + −
PolyP:AMP phosphotransferase + −
required equimolar concentrations of polyphosphate kinase and adenylate kinase (Ischige
and Noguchi, 2000).
In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, massive PolyP:AMP phosphotransferase and PolyP:ADP
phosphotransferase activities were found (Ishige and Noguchi, 2001). Partially purified
PolyP:ADP phosphotransferase was independent of polyphosphate kinase encoded by the
ppk1 gene and could act as a PolyP-dependent nucleoside diphosphate kinase, which pre-
ferred GDP as a phosphate aceptor (Ishige and Noguchi, 2001). It has been demonstrated that
PolyP:AMP phosphotransferase activity in this bacterium originated mainly from the com-
bined action of PolyP:ADP phosphotransferase and adenylate kinase (Ishige and Noguchi,
2001). The PolyP:ADP phosphotransferase activity is probably due to a new polyphosphate
ATP PolyP
(NTP) 1
4
2
5 3
2
ADP
3
NADP
Glucose-6-phosphate
Figure 6.7 Enzymes coupling metabolism of PolyPs and nucleoside phosphates in bacteria:
(1) polyphosphate kinases; (2) glucokinases; (3) NAD kinases; (4) PolyP:AMP phosphotransferase;
(5) adenylate kinase.