Page 148 - The Biochemistry of Inorganic Polyphosphates
P. 148
WU095/Kulaev
WU095-08
Peculiarities of polyphosphate metabolism
132 March 9, 2004 20:32 Char Count= 0
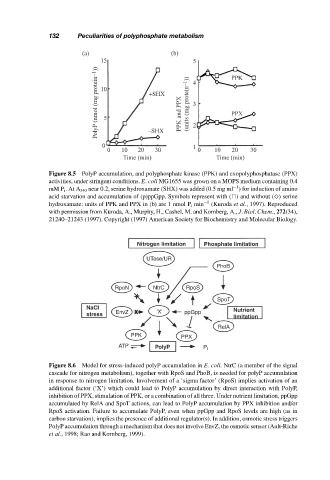
(a) (b)
15 5 PPK
PolyP (nmol (mg protein −1 )) 10 5 +SHX PPK and PPX (units (mg protein −1 )) 4 3 PPX
0 −SHX 2 1
0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30
Time (min) Time (min)
Figure 8.5 PolyP accumulation, and polyphosphate kinase (PPK) and exopolyphosphatase (PPX)
activities, under stringent conditions. E. coli MG1655 was grown on a MOPS medium containing 0.4
−1
mM P i .AtA 540 near 0.2, serine hydroxamate (SHX) was added (0.5 mg ml ) for induction of amino
acid starvation and accumulation of (p)ppGpp. Symbols represent with ( ) and without (♦) serine
hydroxamate: units of PPK and PPX in (b) are 1 nmol P i min −1 (Kuroda et al., 1997). Reproduced
with permission from Kuroda, A., Murphy, H., Cashel, M. and Kornberg, A., J. Biol. Chem., 272(34),
21240–21243 (1997). Copyright (1997) American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
Nitrogen limitation Phosphate limitation
UTase/UR
PhoB
RpoN NtrC RpoS
SpoT
NaCl Nutrient
stress EnvZ ppGpp limitation
RelA
PPK PPX
ATP PolyP P i
Figure 8.6 Model for stress-induced polyP accumulation in E. coli. NtrC (a member of the signal
cascade for nitrogen metabolism), together with RpoS and PhoB, is needed for polyP accumulation
in response to nitrogen limitation. Involvement of a ‘sigma factor’ (RpoS) implies activation of an
additional factor (‘X’) which could lead to PolyP accumulation by direct interaction with PolyP,
inhibition of PPX, stimulation of PPK, or a combination of all three. Under nutrient limitation, ppGpp
accumulated by RelA and SpoT actions, can lead to PolyP accumulation by PPX inhibition and/or
RpoS activation. Failure to accumulate PolyP, even when ppGpp and RpoS levels are high (as in
carbon starvation), implies the presence of additional regulator(s). In addition, osmotic stress triggers
PolyP accumulation through a mechanism that does not involve EnvZ, the osmotic sensor (Ault-Riche
et al., 1998; Rao and Kornberg, 1999).