Page 165 - The Biochemistry of Inorganic Polyphosphates
P. 165
March 9, 2004
20:32
Char Count= 0
WU095-08
WU095/Kulaev
Yeast 149
(a) 6 ∑P
OP
Cells (n × 10 7 ml −1 ) OP (µg P × 10 3 (2 l sample) −1 ) 10 PL (µg P × 10 3 (2 l sample) −1 ) 4 3 2 ∑P (g P × 10 4 (2 l sample) −1 ) 7 4 1 PL
5
3
5
2
(b) 4 1 90 120 150 180 210
PP 1 and PP 2 (µg P × 10 3 ) 3 RNA (µg × 10 5 ); DNA (µg × 0.5 × 10 5 ) 2 1 (mE × 10) PPase (3.6.6.1) 10 PP 2 1
RNA
PP
PPase
5
1 2 DNA
(c) 120 180 PP 4 210
PP (µg P × 10 3 ); ∑PolyP (µg P × 10 4 ) 4 5 × 10 3 ) 10 7 PolyPase (3.6.1.1) (mE × 10) 15 ∑PolyP
PP
3
PP 3 (µg P 9
10
8
3
2
5
1
6
120 150 PolyPase
180
Time (min)
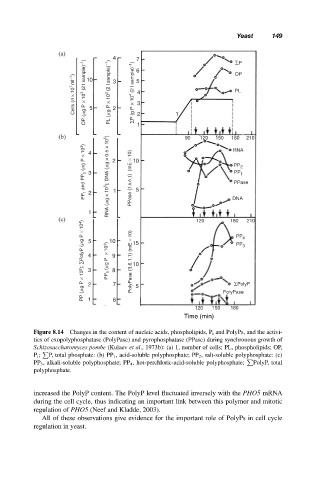
Figure 8.14 Changes in the content of nucleic acids, phospholipids, P i and PolyPs, and the activi-
ties of exopolyphosphatase (PolyPase) and pyrophosphatase (PPase) during synchronous growth of
Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Kulaev et al., 1973b): (a) 1, number of cells; PL, phospholipids; OP,
P i ; P, total phosphate: (b) PP 1 , acid-soluble polyphosphate; PP 2 , salt-soluble polyphosphate: (c)
PP 3 , alkali-soluble polyphosphate; PP 4 , hot-perchloric-acid-soluble polyphosphate; PolyP, total
polyphosphate.
increased the PolyP content. The PolyP level fluctuated inversely with the PHO5 mRNA
during the cell cycle, thus indicating an important link between this polymer and mitotic
regulation of PHO5 (Neef and Kladde, 2003).
All of these observations give evidence for the important role of PolyPs in cell cycle
regulation in yeast.