Page 187 - The Biochemistry of Inorganic Polyphosphates
P. 187
Char Count= 0
20:32
March 9, 2004
WU095-08
WU095/Kulaev
Algae 171
200
1
2
160
120
80
ΣPolyP
40
(g of dry biomass) 6.0
7.0
5.0
P 4.0 PP i
µmol 3.0
2.0
1.0
ATP
0.8
0.6
0.4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Time (d)
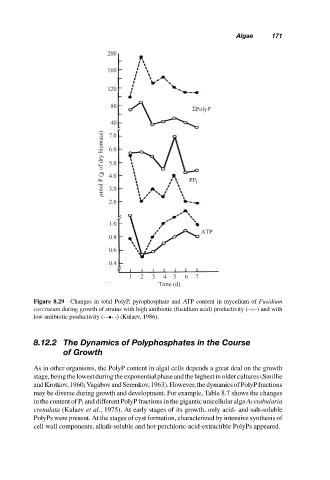
Figure 8.29 Changes in total PolyP, pyrophosphate and ATP content in mycelium of Fusidium
coccineum during growth of strains with high antibiotic (fusidium acid) productivity (–◦–) and with
low antibiotic productivity (- -•- -) (Kulaev, 1986).
8.12.2 The Dynamics of Polyphosphates in the Course
of Growth
As in other organisms, the PolyP content in algal cells depends a great deal on the growth
stage, being the lowest during the exponential phase and the highest in older cultures (Smillie
andKrotkov,1960;VagabovandSerenkov,1963).However,thedymanicsofPolyPfractions
may be diverse during growth and development. For example, Table 8.7 shows the changes
in the content of P i and different PolyP fractions in the gigantic unicellular alga Acetabularia
crenulata (Kulaev et al., 1975). At early stages of its growth, only acid- and salt-soluble
PolyPs were present. At the stages of cyst formation, characterized by intensive synthesis of
cell wall components, alkali-soluble and hot-perchloric-acid-extractible PolyPs appeared.