Page 66 - The Biochemistry of Inorganic Polyphosphates
P. 66
WU095/Kulaev
WU095-04
Forms of polyphosphates cells
50 March 9, 2004 15:30 Char Count= 0
− −
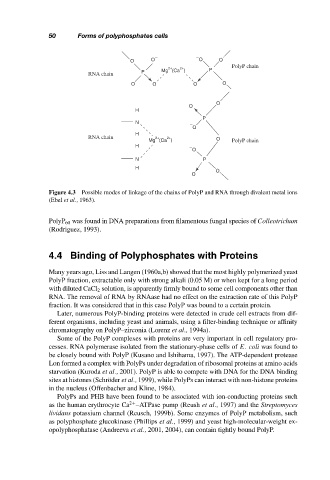
O O O O
2+ 2+ P PolyP chain
Mg (Ca )
RNA chain P
O O O O
O
O
H
P
N −
O
H
RNA chain 2+ 2+ O
Mg (Ca ) PolyP chain
H −
O
N P
H
O
O
Figure 4.3 Possible modes of linkage of the chains of PolyP and RNA through divalent metal ions
(Ebel et al., 1963).
PolyP 60 was found in DNA preparations from filamentous fungal species of Colleotrichum
(Rodriguez, 1993).
4.4 Binding of Polyphosphates with Proteins
Many years ago, Liss and Langen (1960a,b) showed that the most highly polymerized yeast
PolyP fraction, extractable only with strong alkali (0.05 M) or when kept for a long period
with diluted CaCl 2 solution, is apparently firmly bound to some cell components other than
RNA. The removal of RNA by RNAase had no effect on the extraction rate of this PolyP
fraction. It was considered that in this case PolyP was bound to a certain protein.
Later, numerous PolyP-binding proteins were detected in crude cell extracts from dif-
ferent organisms, including yeast and animals, using a filter-binding technique or affinity
chromatography on PolyP–zirconia (Lorenz et al., 1994a).
Some of the PolyP complexes with proteins are very important in cell regulatory pro-
cesses. RNA polymerase isolated from the stationary-phase cells of E. coli was found to
be closely bound with PolyP (Kusano and Ishihama, 1997). The ATP-dependent protease
Lon formed a complex with PolyPs under degradation of ribosomal proteins at amino acids
starvation (Kuroda et al., 2001). PolyP is able to compete with DNA for the DNA binding
sites at histones (Schr¨oder et al., 1999), while PolyPs can interact with non-histone proteins
in the nucleus (Offenbacher and Kline, 1984).
PolyPs and PHB have been found to be associated with ion-conducting proteins such
2+
as the human erythrocyte Ca –ATPase pump (Reush et al., 1997) and the Streptomyces
lividans potassium channel (Reusch, 1999b). Some enzymes of PolyP metabolism, such
as polyphosphate glucokinase (Phillips et al., 1999) and yeast high-molecular-weight ex-
opolyphosphatase (Andreeva et al., 2001, 2004), can contain tightly bound PolyP.