Page 478 - Bruce Ellig - The Complete Guide to Executive Compensation (2007)
P. 478
464 The Complete Guide to Executive Compensation
The popularity of SARs waned with the spread of stock-for-stock and cashless exercises
of stock options, since the executive ended up with the same number of shares (or cash equiv-
alent) that would have been received through exercise of the SARs as illustrated earlier.
While all three transactions bring a tax deduction to the company, the SAR resulted in a
charge to corporate earnings, whereas the stock-for-stock exchange and cashless exercise did
not. But SARs became more popular when FAS 123R put them and stock options on equal
terms for a charge to the earnings statement. They are also used when the country in which
the optionee resides imposes onerous taxes (typically at time of grant) and/or prohibits hold-
ing the security of a foreign country (or perhaps using foreign currency to purchase those
shares) and also when there is a change of control of the company (see Chapter 6’s discussion
on employment agreements). A typical clause would be 100 percent vesting and automatic
payout of the stock option appreciation in the form of SARs.
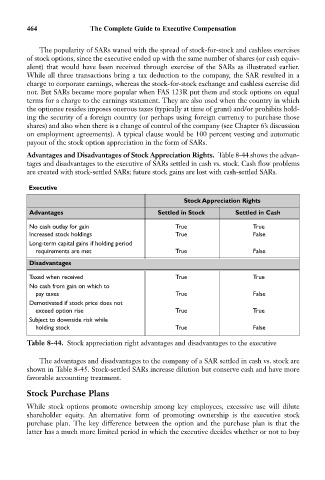
Advantages and Disadvantages of Stock Appreciation Rights. Table 8-44 shows the advan-
tages and disadvantages to the executive of SARs settled in cash vs. stock. Cash flow problems
are created with stock-settled SARs; future stock gains are lost with cash-settled SARs.
Executive
Stock Appreciation Rights
Advantages Settled in Stock Settled in Cash
No cash outlay for gain True True
Increased stock holdings True False
Long-term capital gains if holding period
requirements are met True False
Disadvantages
Taxed when received True True
No cash from gain on which to
pay taxes True False
Demotivated if stock price does not
exceed option rise True True
Subject to downside risk while
holding stock True False
Table 8-44. Stock appreciation right advantages and disadvantages to the executive
The advantages and disadvantages to the company of a SAR settled in cash vs. stock are
shown in Table 8-45. Stock-settled SARs increase dilution but conserve cash and have more
favorable accounting treatment.
Stock Purchase Plans
While stock options promote ownership among key employees, excessive use will dilute
shareholder equity. An alternative form of promoting ownership is the executive stock
purchase plan. The key difference between the option and the purchase plan is that the
latter has a much more limited period in which the executive decides whether or not to buy