Page 132 - The Engineering Guide to LEED-New Construction Sustainable Construction for Engineers
P. 132
112 Cha pte r T h ree
These are compared to determine the points available. The calculations are used to
estimate the total water applied (TWA) for each of these two cases. Note that the total
landscaped areas for both cases must be the same, and it is not appropriate to assume
that the baseline is an entire site with only high water use such as turfgrass. The main
calculation format is reviewed in the following section.
Calculating the Total Water Applied The TWA is determined using a series of landscape
water usage factors and a reference evapotranspiration rate to first determine the
evapotranspiration (ET) rates for both cases (baseline and design). These factors and the
reference rate are as follows:
k The species factor (an indicator of water usage by vegetation species)
s
k The density factor (an indicator of water usage by how densely the vegetation
d
is planted or how substantially the foliage covers the area)
k The microclimate factor (an indicator of water usage with respect to the location
mc
of the vegetation on the site)
ET The reference evapotranspiration rate ET is specific to areas of the country and
0 0
represents a typical evapotranspiration rate based on the local climate and a
reference plant (grass or alfalfa). It is usually also based on conditions in that
area for the month of July since often the greatest irrigation demand is in July.
More information can be obtained from the American Society of Civil Engineers
(ASCE) and the Irrigation Association (IA). Recently, a standardized reference
evapotranspiration equation for the United States has been developed.
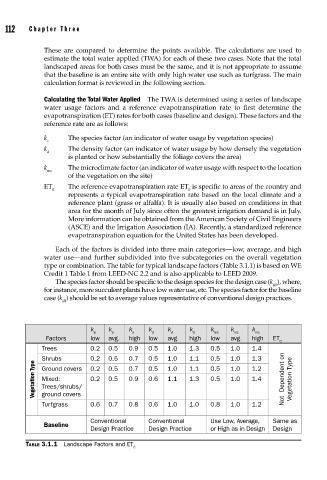
Each of the factors is divided into three main categories—low, average, and high
water use—and further subdivided into five subcategories on the overall vegetation
type or combination. The table for typical landscape factors (Table 3.1.1) is based on WE
Credit 1 Table 1 from LEED-NC 2.2 and is also applicable to LEED 2009.
The species factor should be specific to the design species for the design case (k ), where,
sD
for instance, more succulent plants have low water use, etc. The species factor for the baseline
case (k ) should be set to average values representative of conventional design practices.
sB
k k k k k k k k k
s s s d d d mc mc mc
Factors low avg. high low avg. high low avg. high ET
0
Trees 0.2 0.5 0.9 0.5 1.0 1.3 0.5 1.0 1.4
Shrubs 0.2 0.5 0.7 0.5 1.0 1.1 0.5 1.0 1.3
Vegetation Type Mixed: 0.2 0.5 0.9 0.6 1.1 1.3 0.5 1.0 1.4 Not Dependent on Vegetation Type
0.5
0.7
1.2
0.5
1.0
1.0
1.1
0.5
0.2
Ground covers
Trees/shrubs/
ground covers
Turfgrass 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.6 1.0 1.0 0.8 1.0 1.2
Conventional Conventional Use Low, Average, Same as
Baseline
Design Practice Design Practice or High as in Design Design
TABLE 3.1.1 Landscape Factors and ET
0