Page 347 - The Engineering Guide to LEED-New Construction Sustainable Construction for Engineers
P. 347
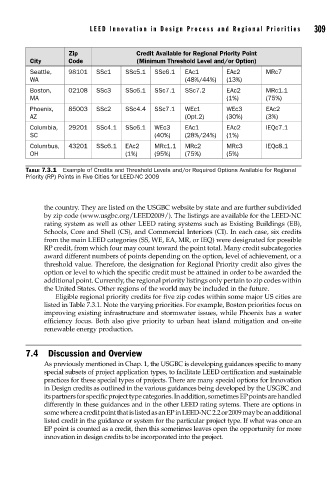
LEED Innovation in Design Pr ocess and Regional Priorities 309
Zip Credit Available for Regional Priority Point
City Code (Minimum Threshold Level and/or Option)
Seattle, 98101 SSc1 SSc5.1 SSc6.1 EAc1 EAc2 MRc7
WA (48%/44%) (13%)
Boston, 02108 SSc3 SSc6.1 SSc7.1 SSc7.2 EAc2 MRc1.1
MA (1%) (75%)
Phoenix, 85003 SSc2 SSc4.4 SSc7.1 WEc1 WEc3 EAc2
AZ (Opt.2) (30%) (3%)
Columbia, 29201 SSc4.1 SSc6.1 WEc3 EAc1 EAc2 IEQc7.1
SC (40%) (28%/24%) (1%)
Columbus, 43201 SSc6.1 EAc2 MRc1.1 MRc2 MRc3 IEQc8.1
OH (1%) (95%) (75%) (5%)
TABLE 7.3.1 Example of Credits and Threshold Levels and/or Required Options Available for Regional
Priority (RP) Points in Five Cities for LEED-NC 2009
the country. They are listed on the USGBC website by state and are further subdivided
by zip code (www.usgbc.org/LEED2009/). The listings are available for the LEED-NC
rating system as well as other LEED rating systems such as Existing Buildings (EB),
Schools, Core and Shell (CS), and Commercial Interiors (CI). In each case, six credits
from the main LEED categories (SS, WE, EA, MR, or IEQ) were designated for possible
RP credit, from which four may count toward the point total. Many credit subcategories
award different numbers of points depending on the option, level of achievement, or a
threshold value. Therefore, the designation for Regional Priority credit also gives the
option or level to which the specific credit must be attained in order to be awarded the
additional point. Currently, the regional priority listings only pertain to zip codes within
the United States. Other regions of the world may be included in the future.
Eligible regional priority credits for five zip codes within some major US cities are
listed in Table 7.3.1. Note the varying priorities. For example, Boston priorities focus on
improving existing infrastructure and stormwater issues, while Phoenix has a water
efficiency focus. Both also give priority to urban heat island mitigation and on-site
renewable energy production.
7.4 Discussion and Overview
As previously mentioned in Chap. 1, the USGBC is developing guidances specific to many
special subsets of project application types, to facilitate LEED certification and sustainable
practices for these special types of projects. There are many special options for Innovation
in Design credits as outlined in the various guidances being developed by the USGBC and
its partners for specific project type categories. In addition, sometimes EP points are handled
differently in these guidances and in the other LEED rating sytems. There are options in
some where a credit point that is listed as an EP in LEED-NC 2.2 or 2009 may be an additional
listed credit in the guidance or system for the particular project type. If what was once an
EP point is counted as a credit, then this sometimes leaves open the opportunity for more
innovation in design credits to be incorporated into the project.