Page 43 - The Geological Interpretation of Well Logs
P. 43
Oo
SELF-POTENTIAL
OR SP LOGS
SPONTANEOUS POTENTIAL
5.1 Generalities
Scale: Millivolis MV LITHOLOGY
The log
50
=~ PH
+
The SP log is a measurement of the natural potential o
differences or self-potentials between an electrode in the
borehole and a reference electrode at the surface: no
artificial currents are applied (Figure 5.2). (The currents
Permeable bed
were actually called ‘potentiels spontanés’, or ‘sponta- R,, ~ salt
R., — fresh
neous potentials’, by Conrad Schlumberger and H.G. Doll
who discovered them.) They originate from the electrical
25m
disequilibrium created by connecting formations vertically
Permeable bed
(in the electrical sense) when in nature they are isolated. R,, — fresh
Ri, 7 salt
Principal uses
The principal uses of the SP log are to calcujate forma-
impermeable bed
tion-water resistivity and to indicate permeability. It can
also be used to estimate shale volume, to indicate facies
som
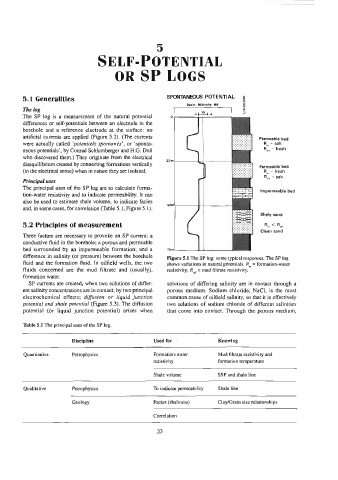
and, in some cases, for correlation (Table 5.1, Figure 5.1). Shaly sand
bed surrounded by an impermeable formation; and a 75m Clean sand
RL <R,
5.2 Principles of measurement
Three factors are necessary to provoke an SP current: a
conductive fluid in the borehole; a porous and permeable
difference in salinity (or pressure) between the borehole
Figure 5.1 The SP tog: some typical responses. The SP log
fluid and the formation fluid. In oilfield wells, the two shows variations in natural potentials. 2, = formation-water
fluids concerned are the mud filtrate and (usually), resistivity, R_, = mud filtrate resistivity.
formation water.
SP currents are created, when two solutions of differ- solutions of differing salinity are in contact through a
ent salinity concentrations are in contact, by two principal} porous medium. Sodium chloride, NaCl, is the most
electrochemical effects; diffusion or liguid junction common cause of oilfield salinity, so that it is effectively
potential and shale potential (Figure 5.3). The diffusion two solutions of sodium chloride of different salinities
potential (or liquid junction potential) arises when that come into contact. Through the porous medium,
Table 5.1 The principal uses of the SP log.
Discipline Used for - Knowing
Quantitative Petrophysics Formation-water Mud filtrate resistivity and
resislivity formation temperature
Shale volume SSP and shale line
Qualitative Petrophysics To indicate permeability Shale line
Geology Facies (shaliness) Clay/Grain size relationships
Correlation
33