Page 39 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 39
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 24
24 AMI • Amperian whirl
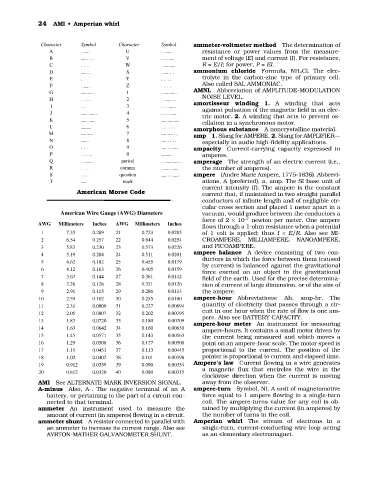
Character Symbol Character Symbol ammeter-voltmeter method The determination of
A . — U . . — resistance or power values from the measure-
B — . . . V . . . — ment of voltage (E) and current (I). For resistance,
C . . . W . —— R = E/I; for power, P = EI.
D — . . X . — . . ammonium chloride Formula, NH 4Cl. The elec-
E . Y . . . . trolyte in the carbon-zinc type of primary cell.
F . — . Z . . . . Also called SAL AMMONIAC.
G —— . 1 . —— . AMNL Abbreviation of AMPLITUDE-MODULATION
H . . . . 2 . . — . . NOISE LEVEL.
amortisseur winding 1. A winding that acts
I . . 3 . . . — .
against pulsation of the magnetic field in an elec-
J — . — . 4 . . . . —
K — . — 5 ——— tric motor. 2. A winding that acts to prevent os-
cillation in a synchronous motor.
L —— 6 . . . . . . amorphous substance A noncrystalline material.
M —— 7 —— . . amp 1. Slang for AMPERE. 2. Slang for AMPLIFIER—
N — . 8 — . . . . especially in audio high-fidelity applications.
O . . 9 — . . — ampacity Current-carrying capacity expressed in
P . . . . . 0 —— amperes.
Q . . — . period . . —— . . amperage The strength of an electric current (i.e.,
R . . . comma . — . — the number of amperes).
S . . . question — . . — . ampere (Andre Marie Ampere, 1775-1836). Abbrevi-
T — mark ations, A (preferred), a, amp. The SI base unit of
current intensity (I). The ampere is the constant
current that, if maintained in two straight parallel
conductors of infinite length and of negligible cir-
cular cross section and placed 1 meter apart in a
American Wire Gauge (AWG) Diameters vacuum, would produce between the conductors a
force of 2 × 10 –7 newton per meter. One ampere
AWG Millimeters Inches AWG Millimeters Inches
flows through a 1-ohm resistance when a potential
1 7.35 0.289 21 0.723 0.0285 of 1 volt is applied; thus I = E/R. Also see MI-
2 6.54 0.257 22 0.644 0.0254 CROAMPERE, MILLIAMPERE, NANOAMPERE,
3 5.83 0.230 23 0.573 0.0226 and PICOAMPERE.
4 5.19 0.204 24 0.511 0.0201 ampere balance A device consisting of two con-
ductors in which the force between them (caused
5 4.62 0.182 25 0.455 0.0179
by current) is balanced against the gravitational
6 4.12 0.163 26 0.405 0.0159
force exerted on an object in the gravitational
7 3.67 0.144 27 0.361 0.0142 field of the earth. Used for the precise determina-
8 3.26 0.128 28 0.321 0.0126 tion of current of large dimension, or of the size of
9 2.91 0.115 29 0.286 0.0113 the ampere.
10 2.59 0.102 30 0.255 0.0100 ampere-hour Abbreviations: Ah, amp-hr. The
11 2.31 0.0909 31 0.227 0.00894 quantity of electricity that passes through a cir-
cuit in one hour when the rate of flow is one am-
12 2.05 0.0807 32 0.202 0.00795
pere. Also see BATTERY CAPACITY.
13 1.83 0.0720 33 0.180 0.00709
ampere-hour meter An instrument for measuring
14 1.63 0.0642 34 0.160 0.00630
ampere-hours. It contains a small motor driven by
15 1.45 0.0571 35 0.143 0.00563 the current being measured and which moves a
16 1.29 0.0508 36 0.127 0.00500 point on an ampere-hour scale. The motor speed is
17 1.15 0.0453 37 0.113 0.00445 proportional to the current. The position of the
18 1.02 0.0402 38 0.101 0.00398 pointer is proportional to current and elapsed time.
19 0.912 0.0359 39 0.090 0.00354 Ampere’s law Current flowing in a wire generates
a magnetic flux that encircles the wire in the
20 0.812 0.0320 40 0.080 0.00315
clockwise direction when the current is moving
AMI See ALTERNATE-MARK INVERSION SIGNAL. away from the observer.
A-minus Also, A-. The negative terminal of an A ampere-turn Symbol, NI. A unit of magnetomotive
battery, or pertaining to the part of a circuit con- force equal to 1 ampere flowing in a single-turn
nected to that terminal. coil. The ampere-turns value for any coil is ob-
ammeter An instrument used to measure the tained by multiplying the current (in amperes) by
amount of current (in amperes) flowing in a circuit. the number of turns in the coil.
ammeter shunt A resistor connected in parallel with Amperian whirl The stream of electrons in a
an ammeter to increase its current range. Also see single-turn, current-conducting wire loop acting
AYRTON-MATHER GALVANOMETER SHUNT. as an elementary electromagnet.