Page 42 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 42
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 27
amplitude separator • analog integrator 27
amplitude separator In a television receiver, a cir- an output equal to their sum or difference (in any
cuit that separates the control pulses from the combination), as desired.
composite video signal. analog channel In an ANALOG COMPUTER, an in-
amplitude suppression ratio The ratio of an un- formation channel in which the extreme limits of
desired output of a frequency-modulated (FM) re- data magnitude are fixed, and the data can have
ceiver to the desired output, when the test signal any value between the limits.
is amplitude modulated and frequency modu- analog communications Any form of communica-
lated simultaneously. tions in which a carrier, generally an electromag-
amplitude-versus-frequency distortion Distortion netic wave or high-frequency current, is varied in
resulting from varying gain or attenuation of an a continuous and controlled way by a data-
amplifier or network, with respect to signal fre- containing signal. See ANALOG, 2.
quency. analog computer A computer in which input and
AMTOR A form of amateur-radio data communica- output quantities are represented as points on
tions, in which the accuracy of a group of charac- continuous (or small-increment) scales. To repre-
ters in a message is checked periodically by the sent these quantities, the computer uses voltages
receiving station. If an error appears likely, then or resistances that are proportional to the num-
the receiving station sends an instruction to the bers to be worked on. When the quantities are
transmitting station to retransmit that particular nonelectrical (such as pressure or velocity), they
group of characters. Characters are sent in are made analogous by proportional voltages or
bunches with pauses for possible inquiries from resistances.
the receiving station. analog data 1. Data represented in a quantita-
AM tuner A compact radio receiver unit that han- tively analogous way. Examples are the deflection
dles amplitude-modulated signals and delivers of a movable-coil meter, the positioning of a slider
low-amplitude audio output to a high-fidelity am- on a slide rule, and the setting of a variable resis-
plifier. Compare AM/FM TUNER and FM TUNER. tor to represent the value of a nonelectrical quan-
amu Abbreviation of atomic mass unit. tity. Also see ANALOG. 2. Data displayed along a
amusement robot An electromechanical robot, of- smooth scale of continuous values (as by a
ten computer-controlled, that is intended for use movable-coil meter), rather than in discrete steps
as a toy. (as by a digital meter).
AN- A prefix designator used by American military analog differentiator An analog circuit or device
services to indicate commonality. whose output waveform is the derivative of the
anacoustic Pertaining to the lack of sound or ab- input-signal waveform, with respect to time.
sence of reverberation or transmission of sonic
waves.
analog 1. A quantity that corresponds, point for
point or value for value, to an otherwise unrelated
quantity. Thus, voltage is the analog of water
pressure, and current is the analog of water flow.
2. Varying over a continuous range and, there-
fore, capable of attaining an infinite number of
values or levels. Compare DIGITAL.
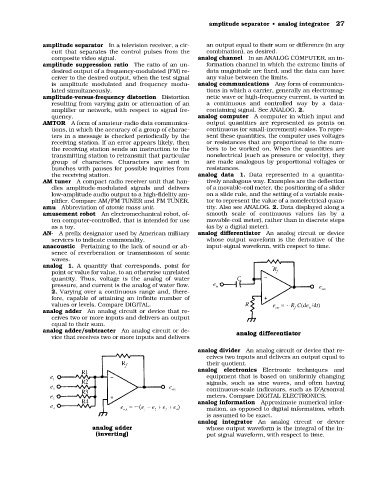
analog adder An analog circuit or device that re-
ceives two or more inputs and delivers an output
equal to their sum.
analog adder/subtracter An analog circuit or de-
vice that receives two or more inputs and delivers
analog divider An analog circuit or device that re-
ceives two inputs and delivers an output equal to
their quotient.
analog electronics Electronic techniques and
equipment that is based on uniformly changing
signals, such as sine waves, and often having
continuous-scale indicators, such as D’Arsonval
meters. Compare DIGITAL ELECTRONICS.
analog information Approximate numerical infor-
mation, as opposed to digital information, which
is assumed to be exact.
analog integrator An analog circuit or device
whose output waveform is the integral of the in-
put signal waveform, with respect to time.