Page 43 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 43
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 28
28 analog inverting adder • AND circuit
that produces an analog record. The counterpart
is a digital recorder, which produces a readout in
discrete numbers (printed or visually displayed).
analog representation Representation of informa-
tion within a smooth, continuous range, rather
than as separate (discrete) steps or points.
analog signal A signal that attains an infinite
number of different amplitude levels, as opposed
to one that can attain only a finite number of lev-
els as a function of time.
analog subtracter An analog circuit or device that
receives two inputs and delivers an output equal
to their difference.
analog summer See ANALOG ADDER.
analog inverting adder An analog adder that de- analog switch A switching device that will only
livers a sum with the opposite sign to that of the pass signals that are faithful analogs of trans-
input quantities. ducer parameters.
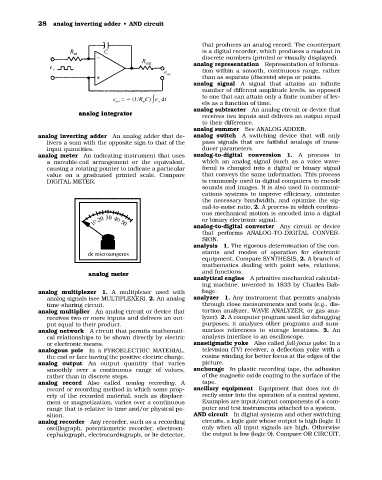
analog meter An indicating instrument that uses analog-to-digital conversion 1. A process in
a movable-coil arrangement or the equivalent, which an analog signal (such as a voice wave-
causing a rotating pointer to indicate a particular form) is changed into a digital or binary signal
value on a graduated printed scale. Compare that conveys the same information. This process
DIGITAL METER. is commonly used in digital computers to encode
sounds and images. It is also used in communi-
cations systems to improve efficiency, minimize
the necessary bandwidth, and optimize the sig-
nal-to-noise ratio. 2. A process in which continu-
ous mechanical motion is encoded into a digital
or binary electronic signal.
analog-to-digital converter Any circuit or device
that performs ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVER-
SION.
analysis 1. The rigorous determination of the con-
stants and modes of operation for electronic
equipment. Compare SYNTHESIS. 2. A branch of
mathematics dealing with point sets, relations,
and functions.
analytical engine A primitive mechanical calculat-
ing machine, invented in 1833 by Charles Bab-
analog multiplexer 1. A multiplexer used with bage.
analog signals (see MULTIPLEXER). 2. An analog analyzer 1. Any instrument that permits analysis
time-sharing circuit. through close measurements and tests (e.g., dis-
analog multiplier An analog circuit or device that tortion analyzer, WAVE ANALYZER, or gas ana-
receives two or more inputs and delivers an out- lyzer). 2. A computer program used for debugging
put equal to their product. purposes; it analyzes other programs and sum-
analog network A circuit that permits mathemati- marizes references to storage locations. 3. An
cal relationships to be shown directly by electric analysis interface to an oscilloscope.
or electronic means. anastigmatic yoke Also called full-focus yoke. In a
analogous pole In a PYROELECTRIC MATERIAL, television (TV) receiver, a deflection yoke with a
the end or face having the positive electric charge. cosine winding for better focus at the edges of the
analog output An output quantity that varies picture.
smoothly over a continuous range of values, anchorage In plastic recording tape, the adhesion
rather than in discrete steps. of the magnetic oxide coating to the surface of the
analog record Also called analog recording. A tape.
record or recording method in which some prop- ancillary equipment Equipment that does not di-
erty of the recorded material, such as displace- rectly enter into the operation of a central system.
ment or magnetization, varies over a continuous Examples are input/output components of a com-
range that is relative to time and/or physical po- puter and test instruments attached to a system.
sition. AND circuit In digital systems and other switching
analog recorder Any recorder, such as a recording circuits, a logic gate whose output is high (logic 1)
oscillograph, potentiometric recorder, electroen- only when all input signals are high. Otherwise
cephalograph, electrocardiograph, or lie detector, the output is low (logic 0). Compare OR CIRCUIT.