Page 52 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 52
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 37
apogee • arc cosecant 37
apogee 1. The point at which an earth-orbiting appliance Electrical equipment in general. This
satellite attains its highest altitude. It occurs might include any home-operated device.
once for every complete orbit. At this point, the application A task or job for which an electronic
satellite travels slower than at any other point in device or system is used. It especially pertains to
the orbit. 2. The altitude, measured from the personal-computer software that has practical
earth’s surface or the earth’s center, of an earth- usefulness.
orbiting satellite at its most distant point. application factor A factor involved in determin-
A power supply A term sometimes used to denote ing the failure rate of a circuit or system affected
the unit that supplies energy to a vacuum-tube by unusual operating conditions.
filament. Compare B POWER SUPPLY. application schematic diagram A diagram of pic-
apparent bearing In radio-direction finding, the torial symbols and lines that illustrate the inter-
uncorrected direction from which a signal ap- relationship of functional circuit blocks in a
pears to arrive. specific program mode.
apparent power In an ac circuit, the power value applicators 1. In dielectric heating, the electrodes
obtained by multiplying the current by voltage (P between which the dielectric body is placed and
equals IE), with no consideration of the effects of the electrostatic field developed. 2. In medical
phase angle. Compare TRUE POWER. electronics, the electrodes applied to a patient
apparent power loss The loss in an ammeter or undergoing diathermy or ultrasonic therapy.
voltmeter, caused by the imperfection of the in- applied voltage The voltage presented to a circuit
strument. At full scale, the ammeter has a certain point or system input, as opposed to the voltage
voltage across its terminals; the apparent power drop resulting from current flow through an ele-
loss is the current multiplied by this voltage. A ment.
voltmeter carries a small current; the apparent applique circuit A circuit for adapting equipment
power loss is the product of the current and the to a specialized job.
indicated voltage. approach-control radar A radar installation serv-
appearance potential The potential through ing a ground-controlled approach (GCA) system.
which an electron must move to produce a cer- approximate data 1. Data obtained through phys-
tain ion from the atom with which it is associated. ical measurements. Such data can never be ex-
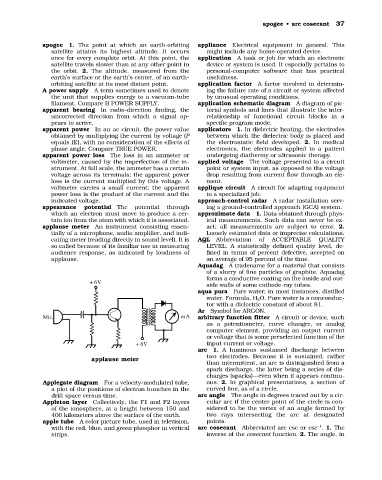
applause meter An instrument consisting essen- act; all measurements are subject to error. 2.
tially of a microphone, audio amplifier, and indi- Loosely estimated data or imprecise calculations.
cating meter (reading directly in sound level). It is AQL Abbreviation of ACCEPTABLE QUALITY
so called because of its familiar use in measuring LEVEL. A statistically defined quality level, de-
audience response, as indicated by loudness of fined in terms of percent defective, accepted on
applause. an average of 95 percent of the time.
Aquadag A tradename for a material that consists
of a slurry of fine particles of graphite. Aquadag
forms a conductive coating on the inside and out-
side walls of some cathode-ray tubes.
aqua pura Pure water; in most instances, distilled
water. Formula, H 2O. Pure water is a nonconduc-
tor with a dielectric constant of about 81.
Ar Symbol for ARGON.
arbitrary function fitter A circuit or device, such
as a potentiometer, curve changer, or analog
computer element, providing an output current
or voltage that is some preselected function of the
input current or voltage.
arc 1. A luminous sustained discharge between
two electrodes. Because it is sustained, rather
than intermittent, an arc is distinguished from a
spark discharge, the latter being a series of dis-
charges (sparks)—even when it appears continu-
Applegate diagram For a velocity-modulated tube, ous. 2. In graphical presentations, a section of
a plot of the positions of electron bunches in the curved line, as of a circle.
drift space versus time. arc angle The angle in degrees traced out by a cir-
Appleton layer Collectively, the F1 and F2 layers cular arc if the center point of the circle is con-
of the ionosphere, at a height between 150 and sidered to be the vertex of an angle formed by
400 kilometers above the surface of the earth. two rays intersecting the arc at designated
apple tube A color picture tube, used in television, points.
–1
with the red, blue, and green phosphor in vertical arc cosecant Abbreviated arc csc or csc . 1. The
strips. inverse of the cosecant function. 2. The angle, in