Page 55 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 55
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 40
40 arm • arsenic
arm 1. Any of the distinct branches of a circuit or
network. Also called leg. 2. A movable element in a
device, usually containing a contact for switching.
armature 1. The rotating member of a motor. 2.
The rotating member of some types of electro-me-
chanical generator. 3. The movable member of a
relay, bell, buzzer, or gong. 4. The movable mem-
ber of an actuator. 5. The soft-iron keeper placed
across the poles of a permanent magnet to con-
serve power.
armature coil A coil of insulated wire wound on a
ferromagnetic core to provide the electromagnetic
properties of an armature. In a motor or genera-
tor, the armature coil is distinguished from the
FIELD COIL.
armature core The ferromagnetic core upon which
the armature coil of a motor or generator is
wound.
armature gap 1. In a motor or generator, the space
between an armature core and the pole of a field
magnet. 2. In a relay, the space between the ar-
mature and the relay-coil core.
armature hesitation A momentary delay in the
movement of a relay.
armature-hesitation contact chatter Undesired
(usually rapid, repetitive) making and breaking of
relay contacts. Generally caused by armature
hesitation.
armature-impact contact chatter Undesired ARPA Acronym for Advanced Research Projects
(usually rapid, repetitive) making and breaking of Agency, a subsidiary of the U.S. Department of
relay contacts, caused by contact bounce when Defense.
the armature strikes the relay core (closure) or array 1. A directive antenna that consists of an as-
backstop (opening). sembly of properly dimensioned and spaced ele-
armature relay A relay that uses an electromagnet ments, such as radiators, directors, and
to pull a lever toward or away from a set of fixed reflectors. 2. A coordinated group or matrix of
contacts. components, such as diodes, resistors, memory
armature travel The distance traveled by an arma- cells, etc., often enclosed in one capsule. 3. Sub-
ture during relay operation. scripted variables representing data arranged so
armor A protective metal cable covering. that a program can examine the array and extract
Armstrong FM system (Edwin H. Armstrong, data relevant to a particular subscript.
1890–1954). A phase-shift method of frequency array device A group of similar or identical compo-
modulation. See PHASE MODULATION. nents that are connected together in a certain
armature voltage control A means of controlling fashion, to perform a specific task.
motor speed by changing the applied armature arrester 1. A device used to protect an installation
winding voltage. from lightning. It consists of a varistor or an air
armchair copy An amateur radio term for recep- gap connected between an antenna or power line
tion of exceptionally clear signals. and an earth ground. The device passes little or
arming the oscilloscope sweep Enabling an oscil- no current under ordinary conditions, but passes
loscope to trigger on the next pulse by closing a heavy current to ground during a lightning
switch. stroke. Also called LIGHTNING ARRESTER. 2. A
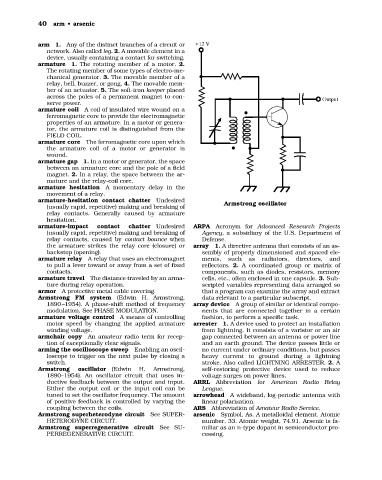
Armstrong oscillator (Edwin H. Armstrong, self-restoring protective device used to reduce
1890–1954). An oscillator circuit that uses in- voltage surges on power lines.
ductive feedback between the output and input. ARRL Abbreviation for American Radio Relay
Either the output coil or the input coil can be League.
tuned to set the oscillator frequency. The amount arrowhead A wideband, log-periodic antenna with
of positive feedback is controlled by varying the linear polarization.
coupling between the coils. ARS Abbreviation of Amateur Radio Service.
Armstrong superheterodyne circuit See SUPER- arsenic Symbol, As. A metalloidal element. Atomic
HETERODYNE CIRCUIT. number, 33. Atomic weight, 74.91. Arsenic is fa-
Armstrong superregenerative circuit See SU- miliar as an n-type dopant in semiconductor pro-
PERREGENERATIVE CIRCUIT. cessing.