Page 60 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 60
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 45
atomic reactor • attracted-disk electrometer 45
atomic reactor See REACTOR, 2. attenuate To reduce in amplitude.
atomic theory The scientific theory that all matter is attenuation A reduction of signal amplitude.
composed ultimately of atoms, which are the small- attenuation characteristic Also called attenua-
est particles retaining the identity of an element. tion constant. 1. In an amplifier, network, or com-
Atoms combine to form molecules, the smallest ponent, the decrease in signal amplitude as a
particles that retain the identity of a compound. function of frequency, usually expressed in deci-
Atoms themselves contain minute subatomic parti- bels per octave. 2. In a transmission line, the de-
cles, some of which carry electric charges. See crease in signal amplitude per unit length.
BOHR ATOM and RUTHERFORD ATOM. Usually expressed in decibels per 100 feet, deci-
atomic time 1. A means of time determination bels per mile, or decibels per kilometer.
that makes use of the resonant vibrations of cer- attenuation constant See ATTENUATION
tain substances, such as cesium. 2. Synchro- CHARACTERISTIC.
nized astronomical time, as determined by an attenuation distortion A type of distortion char-
ATOMIC CLOCK. acterized by variation of attenuation with fre-
atomic unit of energy In a hydrogen atom, the po- quency within a given frequency range.
tential energy of the electron in the lowest-energy attenuation equalizer An equalizer that stabilizes
shell, as averaged over a certain length of time. the transfer impedance between two ports at all
The shell represents the mean energy of the elec- frequencies within a specified frequency band.
tron. attenuation-frequency distortion Distortion
atomic weight 1. The mass of a particular atom in characterized by the attenuation of the frequency
ATOMIC MASS UNITS (amu). 2. A number char- components in a complex waveform. Frequency-
acterizing the average mass of individual atoms sensitive RC networks (such as a Wien bridge) ex-
for a specific isotope of an element. Thus, carbon hibit this type of distortion when they attenuate a
12 (C12) has an atomic weight of 12, oxygen 16 fundamental and each harmonic unequally.
(O16) has an atomic weight of approximately 16, attenuation network A combination of compo-
and uranium 238 (U238) has an atomic weight of nents (R, C, or L singly or in any necessary
about 238. combination) that provide constant signal
atomistics The science of the atom and atomic en- attenuation with negligible phase shift through-
ergy. Also called atomics. out a frequency band.
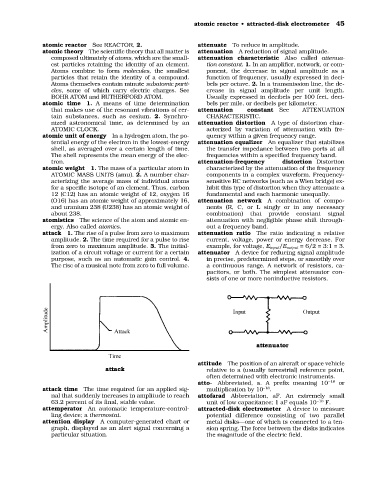
attack 1. The rise of a pulse from zero to maximum attenuation ratio The ratio indicating a relative
amplitude. 2. The time required for a pulse to rise current, voltage, power or energy decrease. For
from zero to maximum amplitude. 3. The initial- example, for voltage, E input/E output = 6/2 = 3:1 = 3.
ization of a circuit voltage or current for a certain attenuator A device for reducing signal amplitude
purpose, such as an automatic gain control. 4. in precise, predetermined steps, or smoothly over
The rise of a musical note from zero to full volume. a continuous range. A network of resistors, ca-
pacitors, or both. The simplest attenuator con-
sists of one or more noninductive resistors.
attitude The position of an aircraft or space vehicle
relative to a (usually terrestrial) reference point,
often determined with electronic instruments.
atto- Abbreviated, a. A prefix meaning 10 –18 or
attack time The time required for an applied sig- multiplication by 10 –18 .
nal that suddenly increases in amplitude to reach attofarad Abbreviation, aF. An extremely small
63.2 percent of its final, stable value. unit of low capacitance; 1 aF equals 10 –18 F.
attemperator An automatic temperature-control- attracted-disk electrometer A device to measure
ling device; a thermostat. potential difference consisting of two parallel
attention display A computer-generated chart or metal disks—one of which is connected to a ten-
graph, displayed as an alert signal concerning a sion spring. The force between the disks indicates
particular situation. the magnitude of the electric field.