Page 62 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 62
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 47
audio-frequency meter • audio mixer 47
audio-frequency meter An instrument to measure type sound like a hiss or roar. Compare
frequencies in the audio-frequency spectrum (ap- FREQUENCY-SHIFT KEYING.
proximately 20 Hz to 20 kHz). Three types are audio-frequency-shift modulator A modulator for
commonly used: audio-frequency-shift keying of a signal.
• Analog Gives direct indications of frequency on audio-frequency spectrum The band of frequen-
the scale of a D’Arsonval meter; the usual range cies extending from roughly 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
is 20 Hz to 100 kHz. High-fidelity component specifications extend
• Digital Gives direct indications of frequency by this range somewhat in both directions (e.g., from
means of readout lamps; the usual range is 1 Hz 10 Hz to 50 kHz).
to 15 MHz. This instrument is useful also as a audio-frequency transformer Abbreviation, AF
radio-frequency meter. transformer. A device used for the purpose of
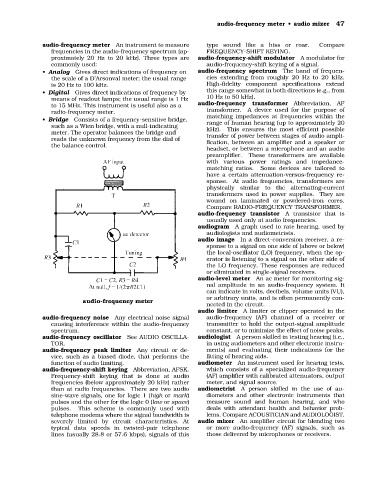
• Bridge Consists of a frequency-sensitive bridge, matching impedances at frequencies within the
such as a Wien bridge, with a null-indicating range of human hearing (up to approximately 20
meter. The operator balances the bridge and kHz). This ensures the most efficient possible
reads the unknown frequency from the dial of transfer of power between stages of audio ampli-
the balance control. fication, between an amplifier and a speaker or
headset, or between a microphone and an audio
preamplifier. These transformers are available
with various power ratings and impedance-
matching ratios. Some devices are tailored to
have a certain attenuation-versus-frequency re-
sponse. At audio frequencies, transformers are
physically similar to the alternating-current
transformers used in power supplies. They are
wound on laminated or powdered-iron cores.
Compare RADIO-FREQUENCY TRANSFORMER.
audio-frequency transistor A transistor that is
usually used only at audio frequencies.
audiogram A graph used to rate hearing, used by
audiologists and audiometrists.
audio image In a direct-conversion receiver, a re-
sponse to a signal on one side of (above or below)
the local-oscillator (LO) frequency, when the op-
erator is listening to a signal on the other side of
the LO frequency. These responses are reduced
or eliminated in single-signal receivers.
audio-level meter An ac meter for monitoring sig-
nal amplitude in an audio-frequency system. It
can indicate in volts, decibels, volume units (VU),
or arbitrary units, and is often permanently con-
nected in the circuit.
audio limiter A limiter or clipper operated in the
audio-frequency noise Any electrical noise signal audio-frequency (AF) channel of a receiver or
causing interference within the audio-frequency transmitter to hold the output-signal amplitude
spectrum. constant, or to minimize the effect of noise peaks.
audio-frequency oscillator See AUDIO OSCILLA- audiologist A person skilled in testing hearing (i.e.,
TOR. in using audiometers and other electronic instru-
audio-frequency peak limiter Any circuit or de- ments) and evaluating their indications for the
vice, such as a biased diode, that performs the fitting of hearing aids.
function of audio limiting. audiometer An instrument used for hearing tests,
audio-frequency-shift keying Abbreviation, AFSK. which consists of a specialized audio-frequency
Frequency-shift keying that is done at audio (AF) amplifier with calibrated attenuators, output
frequencies (below approximately 20 kHz) rather meter, and signal source.
than at radio frequencies. There are two audio audiometrist A person skilled in the use of au-
sine-wave signals, one for logic 1 (high or mark) diometers and other electronic instruments that
pulses and the other for the logic 0 (low or space) measure sound and human hearing, and who
pulses. This scheme is commonly used with deals with attendant health and behavior prob-
telephone modems where the signal bandwidth is lems. Compare ACOUSTICIAN and AUDIOLOGIST.
severely limited by circuit characteristics. At audio mixer An amplifier circuit for blending two
typical data speeds in twisted-pair telephone or more audio-frequency (AF) signals, such as
lines (usually 28.8 or 57.6 kbps), signals of this those delivered by microphones or receivers.