Page 64 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 64
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 49
auroral propagation • automatic chrominance control 49
circuit is at a latitude less than 35 degrees north automated integrated manufacturing system
or south of the equator. Auroral propagation can Acronym, AIMS. An assembly line or factory that
take place at frequencies well above 30 MHz. It is uses robots, often controlled by one or more com-
characterized by deep, rapid fading and random puters, to perform specific tasks that result in the
phase modulation of reflected signals. production of various hardware items.
auroral reflection The return of electromagnetic automatic Self-regulating, independent of human
waves that have been beamed toward an aurora. intervention. Some periodic adjustment might be
Most often observed between 15 MHz and 150 needed.
MHz. automatic base bias A method of obtaining base
authorized access switch A device that disables a bias in a bipolar transistor, where a resistor
security system in a defined region or volume so develops a voltage drop because of the current
that authorized personnel can enter without trig- flowing through it. The resistor is usually placed
gering an alarm condition. in the emitter circuit, raising the emitter above
authorized channel The carrier frequency or band ground potential.
assigned to a transmitting station by a licensing automatic bass compensation Also called bass
authority. Also see RADIO SPECTRUM. boost. In audio high-fidelity systems, a resistor-
autoalarm A device that is actuated from a re- capacitor (RC) network that increases the relative
ceived signal to alert a radio or computer network amplitude of the bass at low volume levels. This
operator to the existence of a message. compensates for the ear’s inefficiency at low fre-
autobaud 1. In digital communications, a function quencies. The function can be automatically ac-
that allows the equipment to adjust itself to the tuated by the setting of the volume control, or it
speed of the terminal. 2. Any digital communica- can be switched manually on and off.
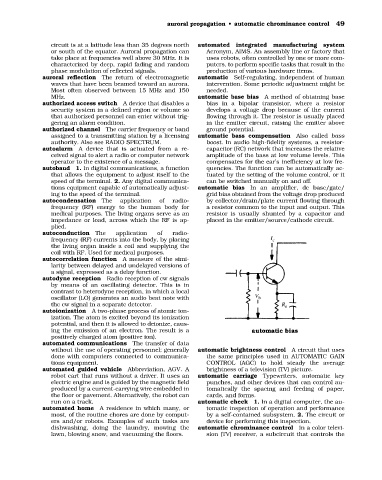
tions equipment capable of automatically adjust- automatic bias In an amplifier, dc base/gate/
ing to the speed of the terminal. grid bias obtained from the voltage drop produced
autocondensation The application of radio- by collector/drain/plate current flowing through
frequency (RF) energy to the human body for a resistor common to the input and output. This
medical purposes. The living organs serve as an resistor is usually shunted by a capacitor and
impedance or load, across which the RF is ap- placed in the emitter/source/cathode circuit.
plied.
autoconduction The application of radio-
frequency (RF) currents into the body, by placing
the living organ inside a coil and supplying the
coil with RF. Used for medical purposes.
autocorrelation function A measure of the simi-
larity between delayed and undelayed versions of
a signal, expressed as a delay function.
autodyne reception Radio reception of cw signals
by means of an oscillating detector. This is in
contrast to heterodyne reception, in which a local
oscillator (LO) generates an audio beat note with
the cw signal in a separate detector.
autoionization A two-phase process of atomic ion-
ization. The atom is excited beyond its ionization
potential, and then it is allowed to deionize, caus-
ing the emission of an electron. The result is a
positively charged atom (positive ion).
automated communications The transfer of data
without the use of operating personnel; generally automatic brightness control A circuit that uses
done with computers connected to communica- the same principles used in AUTOMATIC GAIN
tions equipment. CONTROL (AGC) to hold steady the average
automated guided vehicle Abbreviation, AGV. A brightness of a television (TV) picture.
robot cart that runs without a driver. It uses an automatic carriage Typewriters, automatic key
electric engine and is guided by the magnetic field punches, and other devices that can control au-
produced by a current-carrying wire embedded in tomatically the spacing and feeding of paper,
the floor or pavement. Alternatively, the robot can cards, and forms.
run on a track. automatic check 1. In a digital computer, the au-
automated home A residence in which many, or tomatic inspection of operation and performance
most, of the routine chores are done by comput- by a self-contained subsystem. 2. The circuit or
ers and/or robots. Examples of such tasks are device for performing this inspection.
dishwashing, doing the laundry, mowing the automatic chrominance control In a color televi-
lawn, blowing snow, and vacuuming the floors. sion (TV) receiver, a subcircuit that controls the