Page 61 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 61
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 46
46 attraction • audio-frequency filter
attraction The drawing together or pulling toward, frequency section). 3. A radio channel of fixed fre-
as in the attraction between electric charges or quency that is reserved for voice communica-
magnetic poles. Dissimilar charges and poles at- tions.
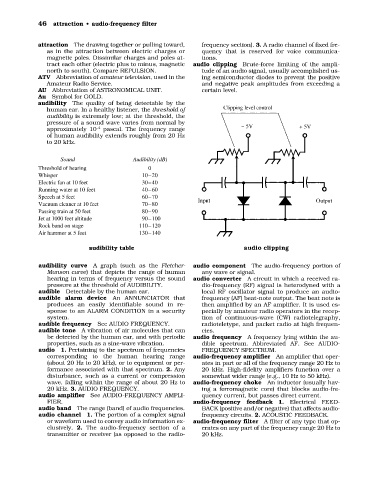
tract each other (electric plus to minus, magnetic audio clipping Brute-force limiting of the ampli-
north to south). Compare REPULSION. tude of an audio signal, usually accomplished us-
ATV Abbreviation of amateur television, used in the ing semiconductor diodes to prevent the positive
Amateur Radio Service. and negative peak amplitudes from exceeding a
AU Abbreviation of ASTRONOMICAL UNIT. certain level.
Au Symbol for GOLD.
audibility The quality of being detectable by the
human ear. In a healthy listener, the threshold of
audibility is extremely low; at the threshold, the
pressure of a sound wave varies from normal by
approximately 10 -4 pascal. The frequency range
of human audibility extends roughly from 20 Hz
to 20 kHz.
Sound Audibility (dB)
Threshold of hearing 0
Whisper 10–20
Electric fan at 10 feet 30–40
Running water at 10 feet 40–60
Speech at 5 feet 60–70
Vacuum cleaner at 10 feet 70–80
Passing train at 50 feet 80–90
Jet at 1000 feet altitude 90–100
Rock band on stage 110–120
Air hammer at 5 feet 130–140
audibility table
audibility curve A graph (such as the Fletcher- audio component The audio-frequency portion of
Munson curve) that depicts the range of human any wave or signal.
hearing in terms of frequency versus the sound audio converter A circuit in which a received ra-
pressure at the threshold of AUDIBILITY. dio-frequency (RF) signal is heterodyned with a
audible Detectable by the human ear. local RF oscillator signal to produce an audio-
audible alarm device An ANNUNCIATOR that frequency (AF) beat-note output. The beat note is
produces an easily identifiable sound in re- then amplified by an AF amplifier. It is used es-
sponse to an ALARM CONDITION in a security pecially by amateur radio operators in the recep-
system. tion of continuous-wave (CW) radiotelegraphy,
audible frequency See AUDIO FREQUENCY. radioteletype, and packet radio at high frequen-
audible tone A vibration of air molecules that can cies.
be detected by the human ear, and with periodic audio frequency A frequency lying within the au-
properties, such as a sine-wave vibration. dible spectrum. Abbreviated AF. See AUDIO-
audio 1. Pertaining to the spectrum of frequencies FREQUENCY SPECTRUM.
corresponding to the human hearing range audio-frequency amplifier An amplifier that oper-
(about 20 Hz to 20 kHz), or to equipment or per- ates in part or all of the frequency range 20 Hz to
formance associated with that spectrum. 2. Any 20 kHz. High-fidelity amplifiers function over a
disturbance, such as a current or compression somewhat wider range (e.g., 10 Hz to 50 kHz).
wave, falling within the range of about 20 Hz to audio-frequency choke An inductor (usually hav-
20 kHz. 3. AUDIO FREQUENCY. ing a ferromagnetic core) that blocks audio-fre-
audio amplifier See AUDIO-FREQUENCY AMPLI- quency current, but passes direct current.
FIER. audio-frequency feedback 1. Electrical FEED-
audio band The range (band) of audio frequencies. BACK (positive and/or negative) that affects audio-
audio channel 1. The portion of a complex signal frequency circuits. 2. ACOUSTIC FEEDBACK.
or waveform used to convey audio information ex- audio-frequency filter A filter of any type that op-
clusively. 2. The audio-frequency section of a erates on any part of the frequency range 20 Hz to
transmitter or receiver (as opposed to the radio- 20 kHz.