Page 54 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 54
5059F-pA_1-55 4/9/01 4:41 PM Page 39
area code • arithmetic symmetry 39
scriber. When making a long-distance call, the argon Symbol, Ar. An inert gaseous element.
area code of the desired station must be given in Atomic number, 18. Atomic weight, 39.94. Argon,
addition to the seven-digit telephone number. present in small amounts in the earth’s atmo-
area protection Coverage of a defined region, in sphere, is used in various specialized devices,
terms of area or volume, by an alarm system. such as lasers.
area redistribution A scheme to determine the ef- argon laser A laser whose tube is filled with argon
fective duration of an irregularly shaped pulse. A gas. It generates coherent light at specific wave-
rectangle is constructed whose height is equal to lengths that are characteristic of elemental ar-
the peak height of the pulse, as displayed on an gon.
oscilloscope. The rectangle width is adjusted un- argument 1. The direction angle of a polar vector.
til the area of the rectangle is the same as the 2. An independent variable whose value deter-
area under the curve representing the pulse. The mines the value of a function.
width of the rectangle then represents the effec- arithmetic address An address obtained by per-
tive duration of the pulse. forming an arithmetic operation on another ad-
area search The scanning of a large group of com- dress.
puter records for those of a major category or arithmetic and logic unit Abbreviation, ALU. The
class. part of a digital computer containing the circuits
area sensor A transducer, used with an alarm sys- that perform calculations and logic operations;
tem, that protects a defined region or volume, distinguished from mass storage, input/output,
such as an office or bedroom. and peripheral units.
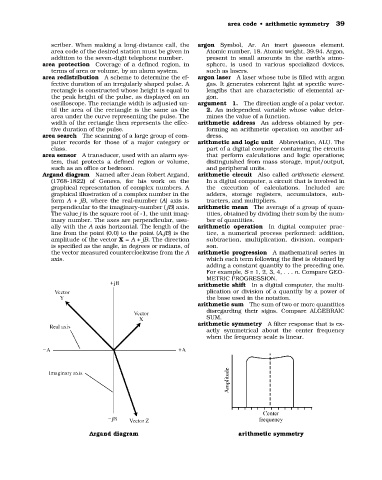
Argand diagram Named after Jean Robert Argand, arithmetic circuit Also called arithmetic element.
(1768-1822) of Geneva, for his work on the In a digital computer, a circuit that is involved in
graphical representation of complex numbers. A the execution of calculations. Included are
graphical illustration of a complex number in the adders, storage registers, accumulators, sub-
form A + jB, where the real-number (A) axis is tracters, and multipliers.
perpendicular to the imaginary-number ( jB) axis. arithmetic mean The average of a group of quan-
The value j is the square root of -1, the unit imag- tities, obtained by dividing their sum by the num-
inary number. The axes are perpendicular, usu- ber of quantities.
ally with the A axis horizontal. The length of the arithmetic operation In digital computer prac-
line from the point (0,0) to the point (A,jB) is the tice, a numerical process performed: addition,
amplitude of the vector X = A + jB. The direction subtraction, multiplication, division, compari-
is specified as the angle, in degrees or radians, of son.
the vector measured counterclockwise from the A arithmetic progression A mathematical series in
axis. which each term following the first is obtained by
adding a constant quantity to the preceding one.
For example, S = 1, 2, 3, 4, . . . n. Compare GEO-
METRIC PROGRESSION.
arithmetic shift In a digital computer, the multi-
plication or division of a quantity by a power of
the base used in the notation.
arithmetic sum The sum of two or more quantities
disregarding their signs. Compare ALGEBRAIC
SUM.
arithmetic symmetry A filter response that is ex-
actly symmetrical about the center frequency
when the frequency scale is linear.