Page 180 - The Jet Engine
P. 180
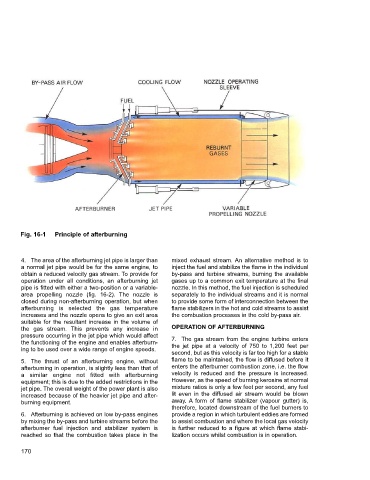
Fig. 16-1 Principle of afterburning
4. The area of the afterburning jet pipe is larger than mixed exhaust stream. An alternative method is to
a normal jet pipe would be for the same engine, to inject the fuel and stabilize the flame in the individual
obtain a reduced velocity gas stream. To provide for by-pass and turbine streams, burning the available
operation under all conditions, an afterburning jet gases up to a common exit temperature at the final
pipe is fitted with either a two-position or a variable- nozzle. In this method, the fuel injection is scheduled
area propelling nozzle (fig. 16-2). The nozzle is separately to the individual streams and it is normal
closed during non-afterburning operation, but when to provide some form of interconnection between the
afterburning is selected the gas temperature flame stabilizers in the hot and cold streams to assist
increases and the nozzle opens to give an exit area the combustion processes in the cold by-pass air.
suitable for the resultant increase in the volume of
the gas stream. This prevents any increase in OPERATION OF AFTERBURNING
pressure occurring in the jet pipe which would affect 7. The gas stream from the engine turbine enters
the functioning of the engine and enables afterburn- the jet pipe at a velocity of 750 to 1,200 feet per
ing to be used over a wide range of engine speeds.
second, but as this velocity is far too high for a stable
5. The thrust of an afterburning engine, without flame to be maintained, the flow is diffused before it
afterburning in operation, is slightly less than that of enters the afterburner combustion zone, i.e. the flow
a similar engine not fitted with afterburning velocity is reduced and the pressure is increased.
equipment; this is due to the added restrictions in the However, as the speed of burning kerosine at normal
jet pipe. The overall weight of the power plant is also mixture ratios is only a few feet per second, any fuel
increased because of the heavier jet pipe and after- lit even in the diffused air stream would be blown
burning equipment. away. A form of flame stabilizer (vapour gutter) is,
therefore, located downstream of the fuel burners to
6. Afterburning is achieved on low by-pass engines provide a region in which turbulent eddies are formed
by mixing the by-pass and turbine streams before the to assist combustion and where the local gas velocity
afterburner fuel injection and stabilizer system is is further reduced to a figure at which flame stabi-
reached so that the combustion takes place in the lization occurs whilst combustion is in operation.
170