Page 163 - The Master Handbook Of Acoustics
P. 163
138 CHAPTER SEVEN
0
Relative octave band level, dB 20
10
30
40
4 kHz
500 Hz
2 kHz
1 kHz
50 Octave Octave Octave Octave
0 0.5 1.0
Time - seconds
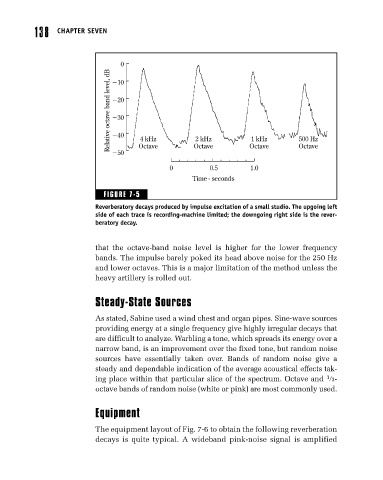
FIGURE 7-5
Reverberatory decays produced by impulse excitation of a small studio. The upgoing left
side of each trace is recording-machine limited; the downgoing right side is the rever-
beratory decay.
that the octave-band noise level is higher for the lower frequency
bands. The impulse barely poked its head above noise for the 250 Hz
and lower octaves. This is a major limitation of the method unless the
heavy artillery is rolled out.
Steady-State Sources
As stated, Sabine used a wind chest and organ pipes. Sine-wave sources
providing energy at a single frequency give highly irregular decays that
are difficult to analyze. Warbling a tone, which spreads its energy over a
narrow band, is an improvement over the fixed tone, but random noise
sources have essentially taken over. Bands of random noise give a
steady and dependable indication of the average acoustical effects tak-
1
ing place within that particular slice of the spectrum. Octave and 3-
octave bands of random noise (white or pink) are most commonly used.
Equipment
The equipment layout of Fig. 7-6 to obtain the following reverberation
decays is quite typical. A wideband pink-noise signal is amplified