Page 208 - The Master Handbook Of Acoustics
P. 208
183
ABSORPTION OF SOUND
wave tube or an impedance tube. No matter what name it bears, it is a
very handy device for quickly and accurately determining coefficients.
It also has the advantage of small size, modest demands in terms of sup-
porting equipment, and it requires only a small sample. This method is
primarily used for porous absorbers because it is not suited to those
absorbers that depend on area for their effect such as vibrating panels
and large slat absorbers.
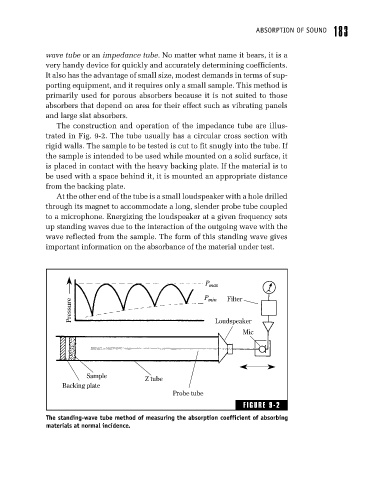
The construction and operation of the impedance tube are illus-
trated in Fig. 9-2. The tube usually has a circular cross section with
rigid walls. The sample to be tested is cut to fit snugly into the tube. If
the sample is intended to be used while mounted on a solid surface, it
is placed in contact with the heavy backing plate. If the material is to
be used with a space behind it, it is mounted an appropriate distance
from the backing plate.
At the other end of the tube is a small loudspeaker with a hole drilled
through its magnet to accommodate a long, slender probe tube coupled
to a microphone. Energizing the loudspeaker at a given frequency sets
up standing waves due to the interaction of the outgoing wave with the
wave reflected from the sample. The form of this standing wave gives
important information on the absorbance of the material under test.
P max
Filter
Pressure P min Loudspeaker
Mic
Sample
Z tube
Backing plate
Probe tube
FIGURE 9-2
The standing-wave tube method of measuring the absorption coefficient of absorbing
materials at normal incidence.