Page 209 - The Master Handbook Of Acoustics
P. 209
184 CHAPTER NINE
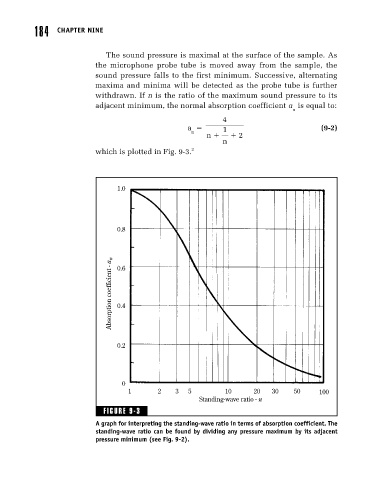
The sound pressure is maximal at the surface of the sample. As
the microphone probe tube is moved away from the sample, the
sound pressure falls to the first minimum. Successive, alternating
maxima and minima will be detected as the probe tube is further
withdrawn. If n is the ratio of the maximum sound pressure to its
adjacent minimum, the normal absorption coefficient a is equal to:
n
4
a (9-2)
1
n
n 2
n
which is plotted in Fig. 9-3. 2
1.0
0.8
Absorption coefficient - a n 0.6
0.4
0.2
0
1 2 3 5 10 20 30 50 100
Standing-wave ratio - n
FIGURE 9-3
A graph for interpreting the standing-wave ratio in terms of absorption coefficient. The
standing-wave ratio can be found by dividing any pressure maximum by its adjacent
pressure minimum (see Fig. 9-2).