Page 158 - The Petroleum System From Source to Trap
P. 158
7. Carbonate Reservoir Rocks 151
INNER SHELF
),G or�SS MIDDLE SHELF
'AW/P,
l),W/P.
MIDDLE SHELF OSH, or
),W/P, 0£P
"l),W/P, or ISLAND
GSH
B 1";n
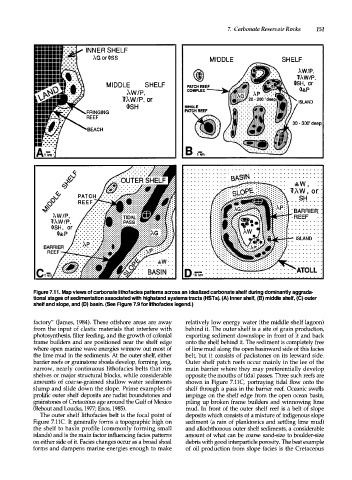
Figure 7.11. Map views of carbonate lithofacies patterns across an idealized carbonate shelf during dominantly aggrada
tional stages of sedimentation associated with highstand systems tracts (HSTs). (A) Inner shelf, (B) middle shelf, (C) outer
sheH and slope, and (D) basin. (See Figure 7.9 for lithofacies legend.)
factory" (James, 1984). These offshore areas are away relatively low energy water (the middle shelf lagoon)
from the input of clastic materials that interfere with behind it. The outer shelf is a site of grain production,
photosynthesis, filter feeding, and the growth of colonial exporting sediment downslope in front of it and back
frame builders and are positioned near the shelf edge onto the shelf behind it. The sediment is completely free
where open marine wave energies winnow out most of of lime mud along the open basin ward side of this facies
the lime mud in the sediments. At the outer shelf, either belt, but it consists of packstones on its leeward side.
barrier reefs or grainstone shoals develop, forming long, Outer shelf patch reefs occur mainly in the lee of the
narrow, nearly continuous lithofacies belts that rim main barrier where they may preferentially develop
shelves or major structural blocks, while considerable opposite the mouths of tidal passes. Three such reefs are
amounts of coarse-grained shallow water sediments shown in Figure 7.11C, portraying tidal flow onto the
slump and slide down the slope. Prime examples of shelf through a pass in the barrier reef. Oceanic swells
prolific outer shelf deposits are rudist boundstones and impinge on the shelf edge from the open ocean basin,
grainstones of Cretaceous age around the Gulf of Mexico piling up broken frame builders and winnowing lime
(Bebout and Loucks, 1977; Enos, 1985). mud. In front of the outer shelf reef is a belt of slope
The outer shelf lithofacies belt is the focal point of deposits which consists of a mixture of indigenous slope
Figure 7.11C. It generally forms a topographic high on sediment (a rain of planktonics and settling lime mud)
the shelf to basin profile (commonly forming small and allochthonous outer shelf sediments, a considerable
islands) and is the main factor influencing facies patterns amount of what can be coarse sand-size to boulder-size
on either side of it. Facies changes occur as a broad shoal debris with good interparticle porosity. The best example
forms and dampens marine energies enough to make of oil production from slope facies is the Cretaceous