Page 142 - The Toyota Way Fieldbook
P. 142
Chapter 6. Establish Standardized Processes and Procedures 119
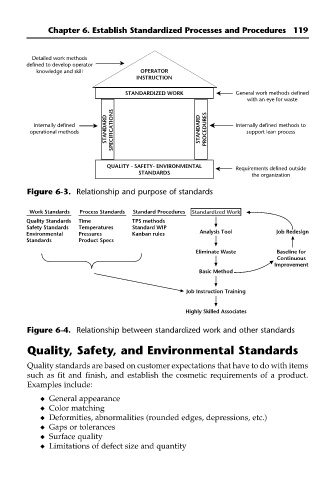
Detailed work methods
defined to develop operator
knowledge and skill OPERATOR
INSTRUCTION
STANDARDIZED WORK General work methods defined
with an eye for waste
STANDARD SPECIFICATIONS STANDARD PROCEDURES
Internally defined Internally defined methods to
operational methods support lean process
QUALITY - SAFETY- ENVIRONMENTAL
Requirements defined outside
STANDARDS
the organization
Figure 6-3. Relationship and purpose of standards
Work Standards Process Standards Standard Procedures Standardized Work
Quality Standards Time TPS methods
Safety Standards Temperatures Standard WIP
Environmental Pressures Kanban rules Analysis Tool Job Redesign
Standards Product Specs
Eliminate Waste Baseline for
Continuous
Improvement
Basic Method
Job Instruction Training
Highly Skilled Associates
Figure 6-4. Relationship between standardized work and other standards
Quality, Safety, and Environmental Standards
Quality standards are based on customer expectations that have to do with items
such as fit and finish, and establish the cosmetic requirements of a product.
Examples include:
◆ General appearance
◆ Color matching
◆ Deformities, abnormalities (rounded edges, depressions, etc.)
◆ Gaps or tolerances
◆ Surface quality
◆ Limitations of defect size and quantity